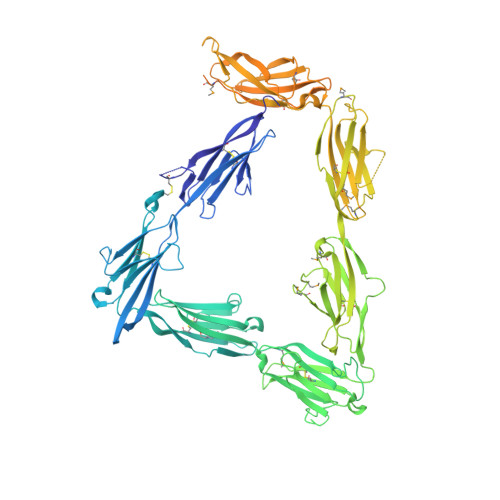
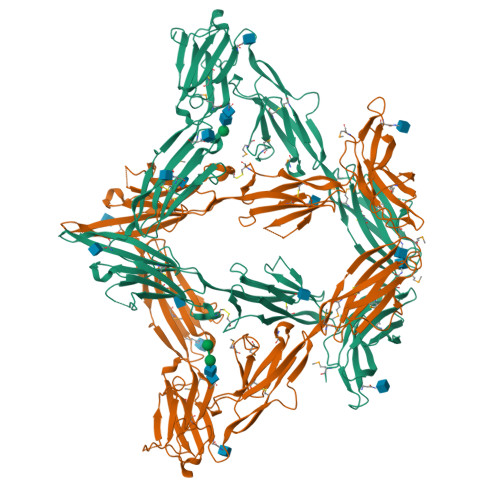
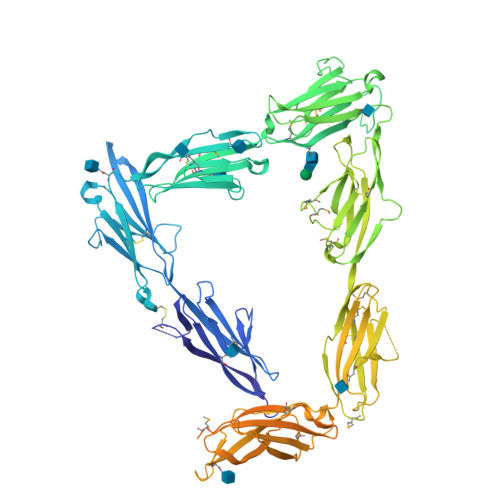
Structural Mechanism for Modulation of Synaptic Neuroligin-Neurexin Signaling by MDGA Proteins.
Elegheert, J., Cvetkovska, V., Clayton, A.J., Heroven, C., Vennekens, K.M., Smukowski, S.N., Regan, M.C., Jia, W., Smith, A.C., Furukawa, H., Savas, J.N., de Wit, J., Begbie, J., Craig, A.M., Aricescu, A.R.(2017) Neuron 95: 896-913.e10
- PubMed: 28817804
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.07.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OJ2, 5OJ6, 5OJK - PubMed Abstract:
Neuroligin-neurexin (NL-NRX) complexes are fundamental synaptic organizers in the central nervous system. An accurate spatial and temporal control of NL-NRX signaling is crucial to balance excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission, and perturbations are linked with neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. MDGA proteins bind NLs and control their function and interaction with NRXs via unknown mechanisms. Here, we report crystal structures of MDGA1, the NL1-MDGA1 complex, and a spliced NL1 isoform. Two large, multi-domain MDGA molecules fold into rigid triangular structures, cradling a dimeric NL to prevent NRX binding. Structural analyses guided the discovery of a broad, splicing-modulated interaction network between MDGA and NL family members and helped rationalize the impact of autism-linked mutations. We demonstrate that expression levels largely determine whether MDGAs act selectively or suppress the synapse organizing function of multiple NLs. These results illustrate a potentially brain-wide regulatory mechanism for NL-NRX signaling modulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford OX3 7BN, UK. Electronic address: jelegheert@strubi.ox.ac.uk.