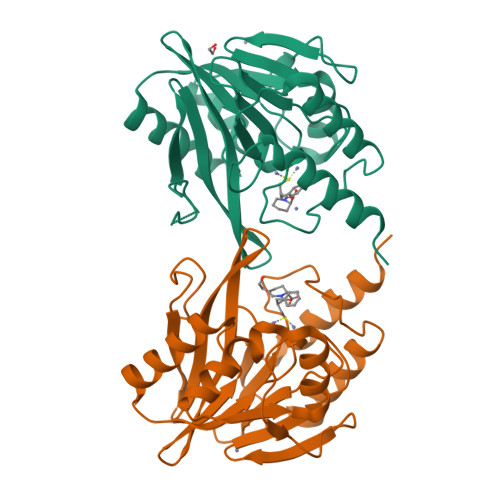
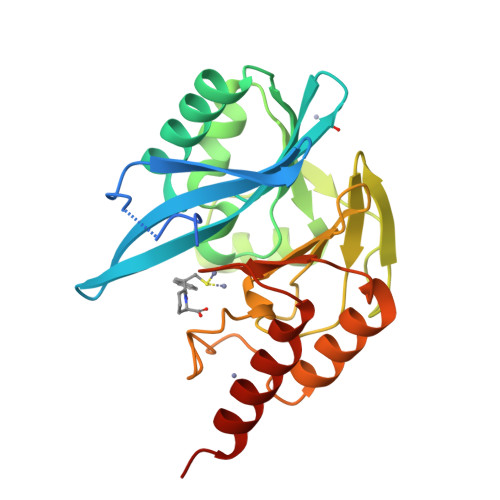
Challenges in the Development of a Thiol-Based Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor for Metallo-beta-Lactamases.
Buttner, D., Kramer, J.S., Klingler, F.M., Wittmann, S.K., Hartmann, M.R., Kurz, C.G., Kohnhauser, D., Weizel, L., Bruggerhoff, A., Frank, D., Steinhilber, D., Wichelhaus, T.A., Pogoryelov, D., Proschak, E.(2018) ACS Infect Dis 4: 360-372
- PubMed: 29172434
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.7b00129
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5O7N - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogens, expressing metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), become resistant against most β-lactam antibiotics. Besides the dragging search for new antibiotics, development of MBL inhibitors would be an alternative weapon against resistant bacterial pathogens. Inhibition of resistance enzymes could restore the antibacterial activity of β-lactams. Various approaches to MBL inhibitors are described; among others, the promising motif of a zinc coordinating thiol moiety is very popular. Nevertheless, since the first report of a thiol-based MBL inhibitor (thiomandelic acid) in 2001, no steps in development of thiol based MBL inhibitors were reported that go beyond clinical isolate testing. In this study, we report on the synthesis and biochemical characterization of thiol-based MBL inhibitors and highlight the challenges behind the development of thiol-based compounds, which exhibit good in vitro activity toward a broad spectrum of MBLs, selectivity against human off-targets, and reasonable activity against clinical isolates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Medical Microbiology and Infection Control , Goethe University Hospital , Paul-Ehrlich-Straße 40 , 60596 Frankfurt , Germany.