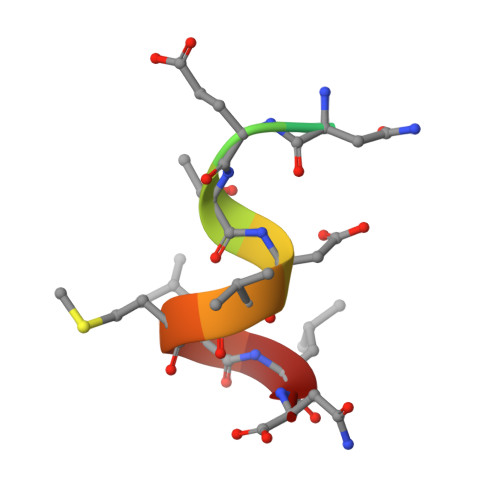
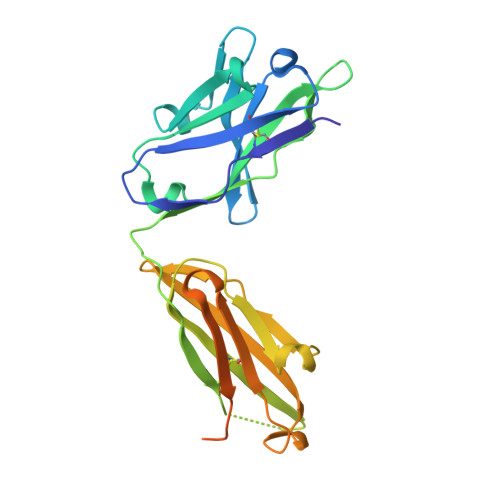
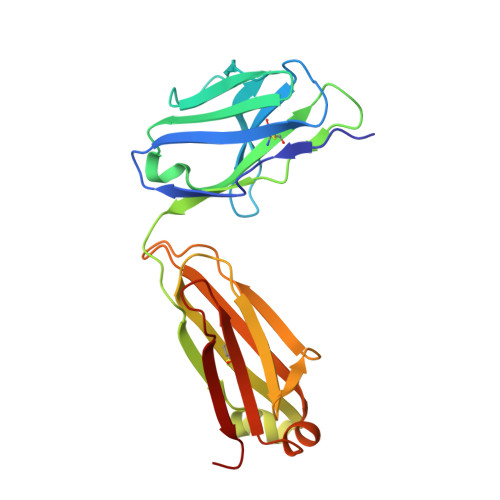
Conformational Flexibility in the Immunoglobulin-Like Domain of the Hepatitis C Virus Glycoprotein E2.
Vasiliauskaite, I., Owsianka, A., England, P., Khan, A.G., Cole, S., Bankwitz, D., Foung, S.K.H., Pietschmann, T., Marcotrigiano, J., Rey, F.A., Patel, A.H., Krey, T.(2017) mBio 8
- PubMed: 28512091
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00382-17
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5NPH, 5NPI, 5NPJ - PubMed Abstract:
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) glycoprotein E2 is the major target of neutralizing antibodies and is therefore highly relevant for vaccine design. Its structure features a central immunoglobulin (Ig)-like β-sandwich that contributes to the binding site for the cellular receptor CD81. We show that a synthetic peptide corresponding to a β-strand of this Ig-like domain forms an α-helix in complex with the anti-E2 antibody DAO5, demonstrating an inside-out flip of hydrophobic residues and a secondary structure change in the composite CD81 binding site. A detailed interaction analysis of DAO5 and cross-competing neutralizing antibodies with soluble E2 revealed that the Ig-like domain is trapped by different antibodies in at least two distinct conformations. DAO5 specifically captures retrovirus particles bearing HCV glycoproteins (HCVpp) and infectious cell culture-derived HCV particles (HCVcc). Infection of cells by DAO5-captured HCVpp can be blocked by a cross-competing neutralizing antibody, indicating that a single virus particle simultaneously displays E2 molecules in more than one conformation on its surface. Such conformational plasticity of the HCV E2 receptor binding site has important implications for immunogen design. IMPORTANCE Recent advances in the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection with direct-acting antiviral drugs have enabled the control of this major human pathogen. However, due to their high costs and limited accessibility in combination with the lack of awareness of the mostly asymptomatic infection, there is an unchanged urgent need for an effective vaccine. The viral glycoprotein E2 contains regions that are crucial for virus entry into the host cell, and antibodies that bind to these regions can neutralize infection. One of the major targets of neutralizing antibodies is the central immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain within E2. We show here that this Ig-like domain is conformationally flexible at the surface of infectious HCV particles and pseudoparticles. Our study provides novel insights into the interactions of HCV E2 with the humoral immune system that should aid future vaccine development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Unité de Virologie Structurale, Department Virologie, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France.