Biophysical characterization and structural determination of the potent cytotoxic Psathyrella asperospora lectin.
Ribeiro, J.P., Ali Abol Hassan, M., Rouf, R., Tiralongo, E., May, T.W., Day, C.J., Imberty, A., Tiralongo, J., Varrot, A.(2017) Proteins 85: 969-975
- PubMed: 28168856
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25265
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5MB4 - PubMed Abstract:
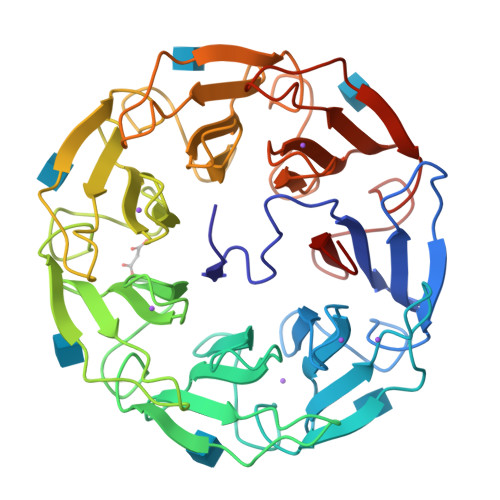
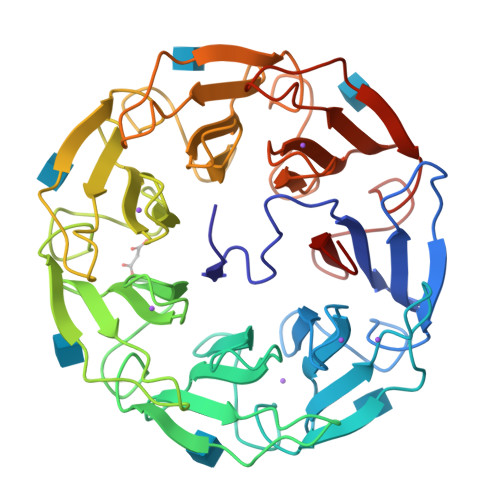
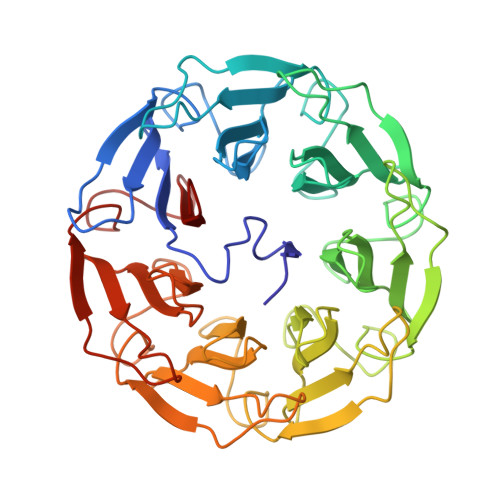
A lectin with strong cytotoxic effect on human colon cancer HT29 and monkey kidney VERO cells was recently identified from the Australian indigenous mushroom Psathyrella asperospora and named PAL. We herein present its biochemical and structural analysis using a multidisciplinary approach. Glycan arrays revealed binding preference towards N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and, to a lesser extent, towards sialic acid (Neu5Ac). Submicromolar and millimolar affinity was measured by surface plasmon resonance for GlcNAc and NeuAc, respectively. The structure of PAL was resolved by X-ray crystallography, elucidating both the protein's amino acid sequence as well as the molecular basis rationalizing its binding specificity. Proteins 2017; 85:969-975. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Organizational Affiliation:
CERMAV, UPR5301, CNRS and Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, 38041, France.