Regulation of the Equilibrium between Closed and Open Conformations of Annexin A2 by N-Terminal Phosphorylation and S100A4-Binding.
Ecsedi, P., Kiss, B., Gogl, G., Radnai, L., Buday, L., Koprivanacz, K., Liliom, K., Leveles, I., Vertessy, B., Jeszenoi, N., Hetenyi, C., Schlosser, G., Katona, G., Nyitray, L.(2017) Structure 25: 1195-1207.e5
- PubMed: 28669632
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.06.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
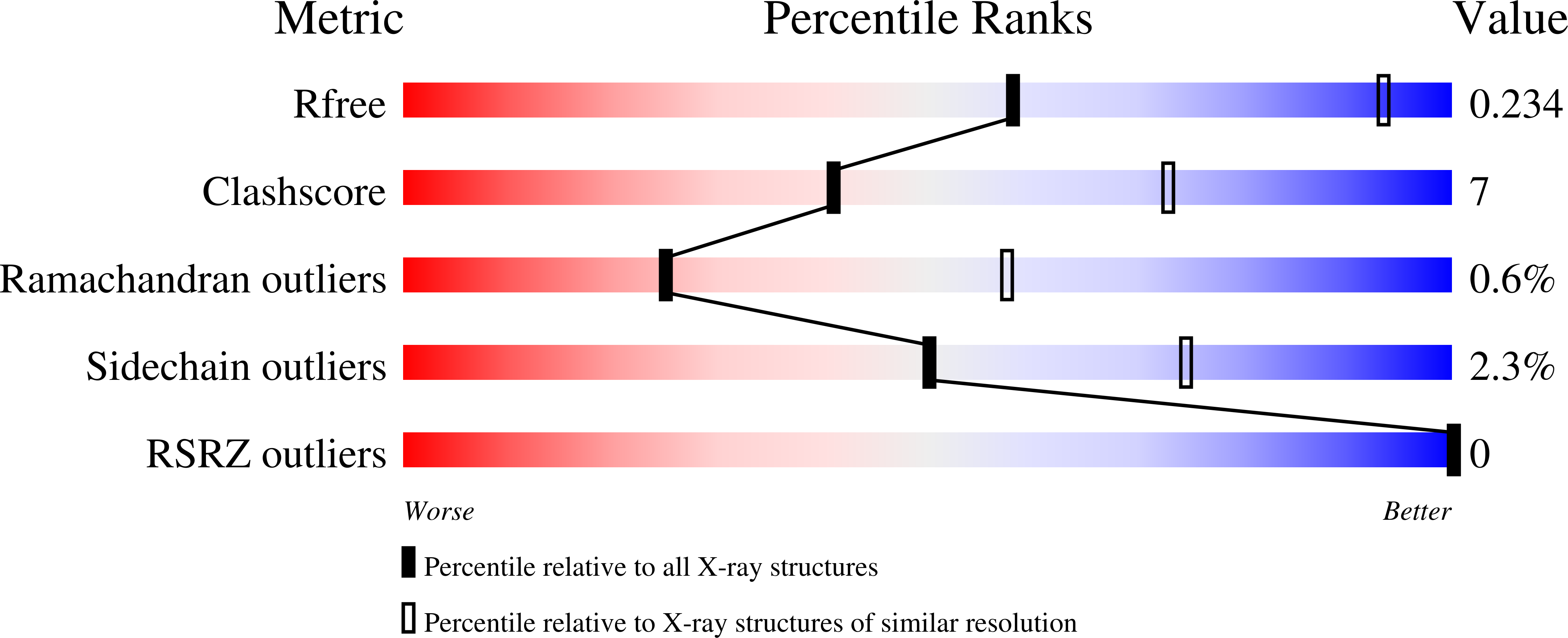
5LPU, 5LPX, 5LQ0, 5LQ2 - PubMed Abstract:
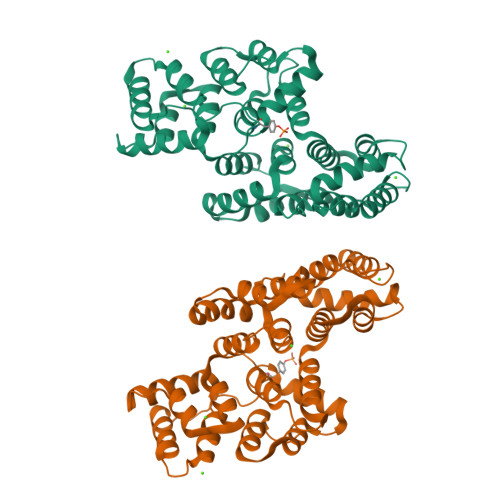
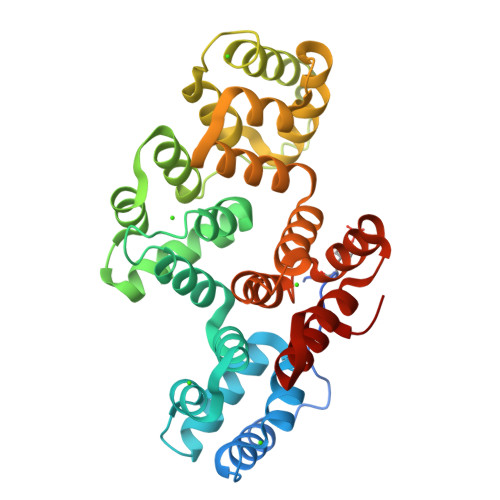
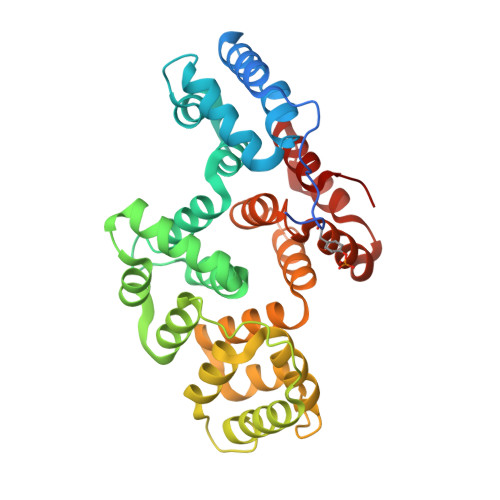
Annexin A2 (ANXA2) has a versatile role in membrane-associated functions including membrane aggregation, endo- and exocytosis, and it is regulated by post-translational modifications and protein-protein interactions through the unstructured N-terminal domain (NTD). Our sequence analysis revealed a short motif responsible for clamping the NTD to the C-terminal core domain (CTD). Structural studies indicated that the flexibility of the NTD and CTD are interrelated and oppositely regulated by Tyr24 phosphorylation and Ser26Glu phosphomimicking mutation. The crystal structure of the ANXA2-S100A4 complex showed that asymmetric binding of S100A4 induces dislocation of the NTD from the CTD and, similar to the Ser26Glu mutation, unmasks the concave side of ANXA2. In contrast, pTyr24 anchors the NTD to the CTD and hampers the membrane-bridging function. This inhibition can be restored by S100A4 and S100A10 binding. Based on our results we provide a structural model for regulation of ANXA2-mediated membrane aggregation by NTD phosphorylation and S100 binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, 1117 Budapest, Hungary.