Structural basis for single-stranded RNA recognition and cleavage by C3PO
Zhang, J., Liu, H., Yao, Q., Yu, X., Chen, Y., Cui, R., Wu, B., Zheng, L., Zuo, J., Huang, Z., Ma, J., Gan, J.(2016) Nucleic Acids Res 44: 9494-9504
- PubMed: 27596600
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw776
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JR9, 5JRC, 5JRE - PubMed Abstract:
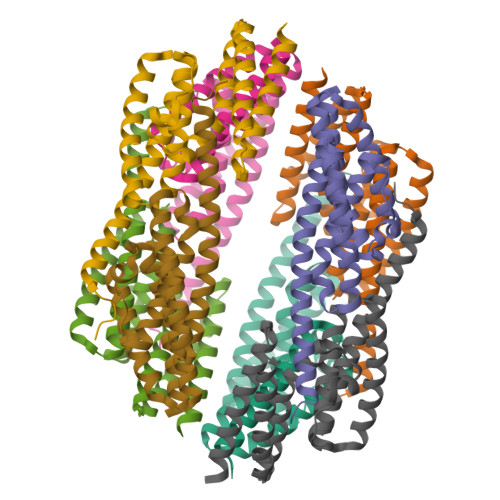
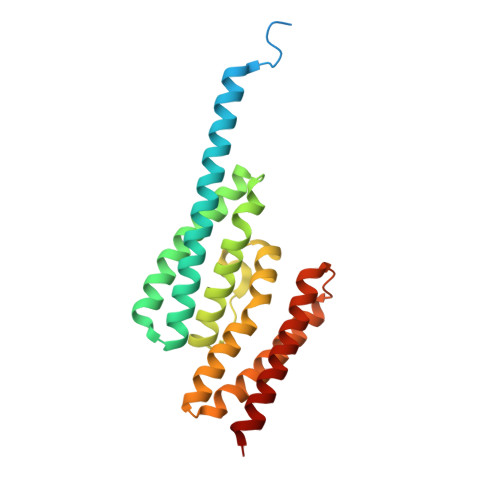
Translin and translin-associated factor-x are highly conserved in eukaroytes; they can form heteromeric complexes (known as C3POs) and participate in various nucleic acid metabolism pathways. In humans and Drosophila, C3POs cleave the fragmented siRNA passenger strands and facilitate the activation of RNA-induced silencing complex, the effector complex of RNA interference (RNAi). Here, we report three crystal structures of Nanoarchaeum equitans (Ne) C3PO. The apo-NeC3PO structure adopts an open form and unravels a potential substrates entryway for the first time. The NeC3PO:ssRNA and NeC3PO:ssDNA complexes fold like closed football with the substrates captured at the inner cavities. The NeC3PO:ssRNA structure represents the only catalytic form C3PO complex available to date; with mutagenesis and in vitro cleavage assays, the structure provides critical insights into the substrate binding and the two-cation-assisted catalytic mechanisms that are shared by eukaryotic C3POs. The work presented here further advances our understanding on the RNAi pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200438, China.