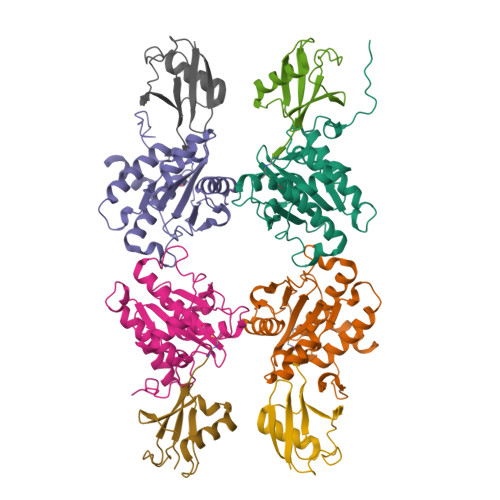
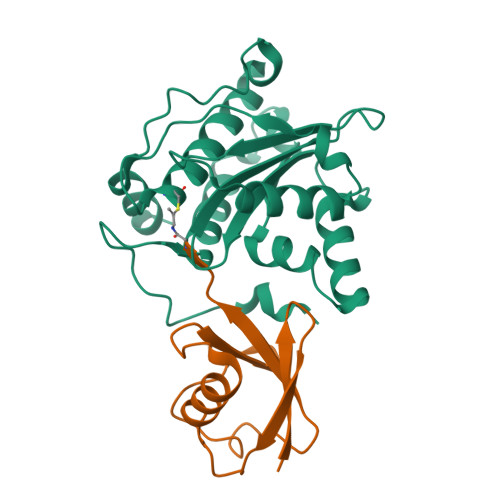
The Molecular Basis for Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Specificities in Bacterial Effector Proteases.
Pruneda, J.N., Durkin, C.H., Geurink, P.P., Ovaa, H., Santhanam, B., Holden, D.W., Komander, D.(2016) Mol Cell 63: 261-276
- PubMed: 27425412
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HAF, 5HAG, 5HAM, 5JP1, 5JP3 - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogenic bacteria rely on secreted effector proteins to manipulate host signaling pathways, often in creative ways. CE clan proteases, specific hydrolases for ubiquitin-like modifications (SUMO and NEDD8) in eukaryotes, reportedly serve as bacterial effector proteins with deSUMOylase, deubiquitinase, or, even, acetyltransferase activities. Here, we characterize bacterial CE protease activities, revealing K63-linkage-specific deubiquitinases in human pathogens, such as Salmonella, Escherichia, and Shigella, as well as ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like cross-reactive enzymes in Chlamydia, Rickettsia, and Xanthomonas. Five crystal structures, including ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like complexes, explain substrate specificities and redefine relationships across the CE clan. Importantly, this work identifies novel family members and provides key discoveries among previously reported effectors, such as the unexpected deubiquitinase activity in Xanthomonas XopD, contributed by an unstructured ubiquitin binding region. Furthermore, accessory domains regulate properties such as subcellular localization, as exemplified by a ubiquitin-binding domain in Salmonella Typhimurium SseL. Our work both highlights and explains the functional adaptations observed among diverse CE clan proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Protein and Nucleic Acid Chemistry, MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK.