Crystal structure of Rv3899c(184-410), a hypothetical protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Liu, Y.Y., Gao, Y.R., Li, D.F., Fleming, J., Li, H.L., Bi, L.J.(2016) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 72: 642-645
- PubMed: 27487929
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X16010943
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5IMU - PubMed Abstract:
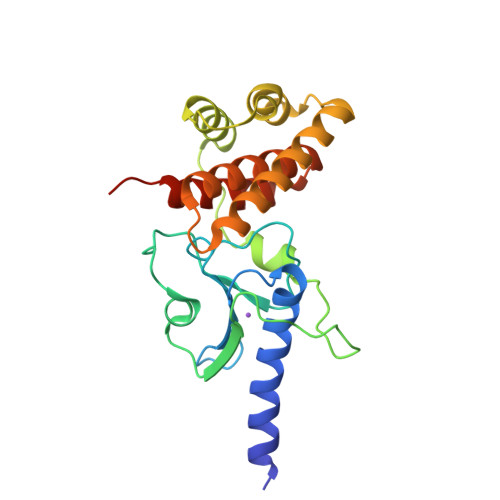
Rv3899c is a hypothetical protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is conserved across mycobacteria. It is predicted to be secreted and has been found in culture filtrates. It has been proposed as a potential vaccine candidate; however, its biological function is unknown. Here, the global structure of Rv3899c(184-410), a fragment of Rv3899c, is reported. The structure resembles the shell of a sea snail, and its N- and C-termini form two relatively independent compact domains: an α/β/α sandwich folding domain and an α-helix bundle domain. There are no reported protein structures for any Rv3899c homologues; this structure provides the first structural glimpse of a new protein family consisting of Rv3899c and its homologues.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shanghai Key Laboratory of New Drug Design, School of Pharmacy, East China University of Science and Technology, 130 Meilong Road, Shanghai 200237, People's Republic of China.