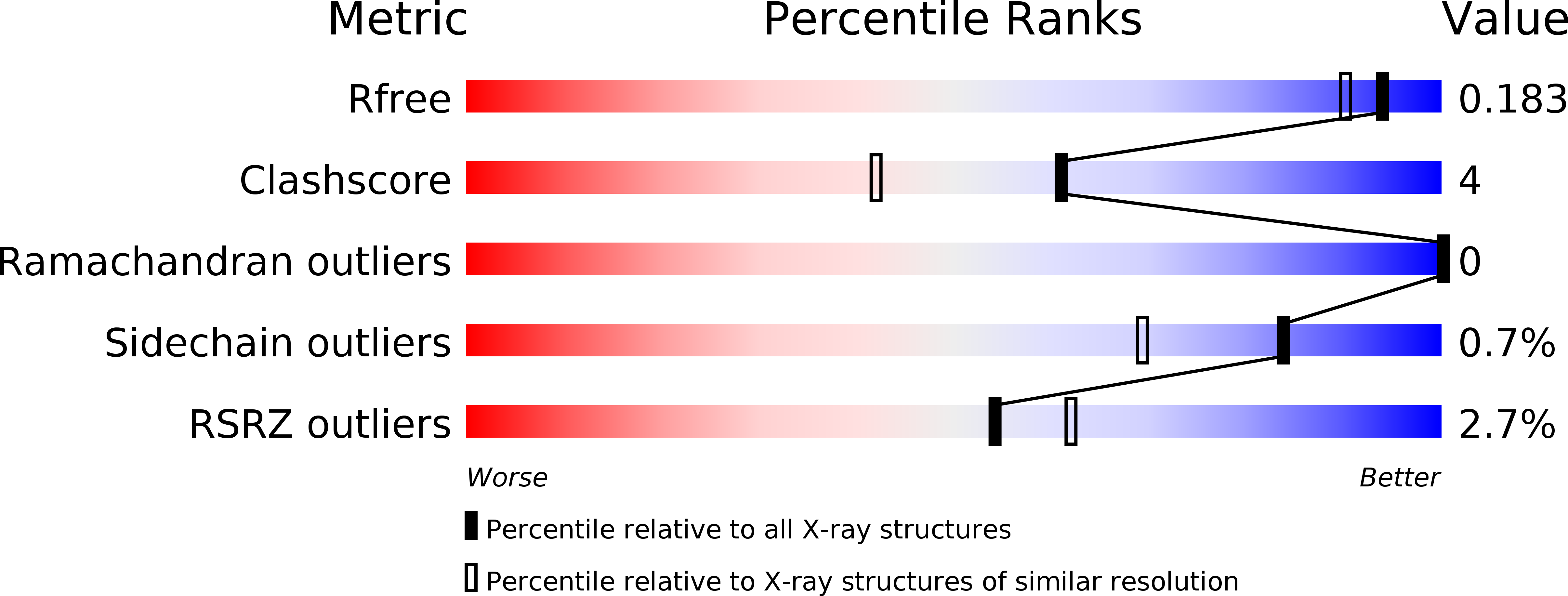
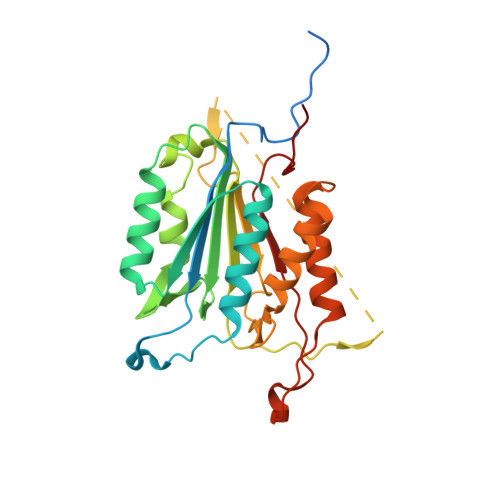
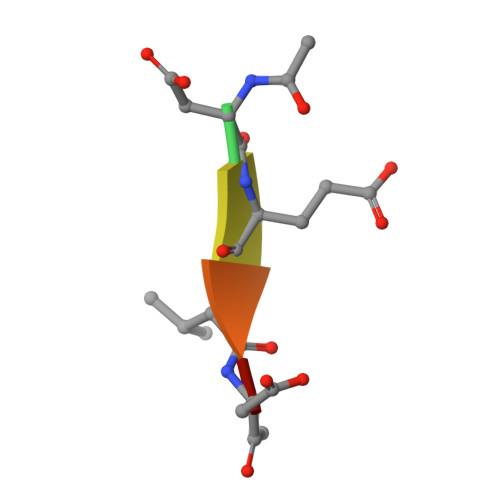
Tunable allosteric library of caspase-3 identifies coupling between conserved water molecules and conformational selection.
Maciag, J.J., Mackenzie, S.H., Tucker, M.B., Schipper, J.L., Swartz, P., Clark, A.C.(2016) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113: E6080-E6088
- PubMed: 27681633
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603549113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5I9B, 5I9T, 5IAB, 5IAE, 5IAG, 5IAJ, 5IAK, 5IAN, 5IAR, 5IAS, 5IBC, 5IBP, 5IBR - PubMed Abstract:
The native ensemble of caspases is described globally by a complex energy landscape where the binding of substrate selects for the active conformation, whereas targeting an allosteric site in the dimer interface selects an inactive conformation that contains disordered active-site loops. Mutations and posttranslational modifications stabilize high-energy inactive conformations, with mostly formed, but distorted, active sites. To examine the interconversion of active and inactive states in the ensemble, we used detection of related solvent positions to analyze 4,995 waters in 15 high-resolution (<2.0 Å) structures of wild-type caspase-3, resulting in 450 clusters with the most highly conserved set containing 145 water molecules. The data show that regions of the protein that contact the conserved waters also correspond to sites of posttranslational modifications, suggesting that the conserved waters are an integral part of allosteric mechanisms. To test this hypothesis, we created a library of 19 caspase-3 variants through saturation mutagenesis in a single position of the allosteric site of the dimer interface, and we show that the enzyme activity varies by more than four orders of magnitude. Altogether, our database consists of 37 high-resolution structures of caspase-3 variants, and we demonstrate that the decrease in activity correlates with a loss of conserved water molecules. The data show that the activity of caspase-3 can be fine-tuned through globally desolvating the active conformation within the native ensemble, providing a mechanism for cells to repartition the ensemble and thus fine-tune activity through conformational selection.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX 76019; Department of Molecular and Structural Biochemistry, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC 27695.