New Helical Binding Domain Mediates a Glycosyltransferase Activity of a Bifunctional Protein.
Zhang, H., Zhou, M., Yang, T., Haslam, S.M., Dell, A., Wu, H.(2016) J Biological Chem 291: 22106-22117
- PubMed: 27539847
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.731695
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5HEC - PubMed Abstract:
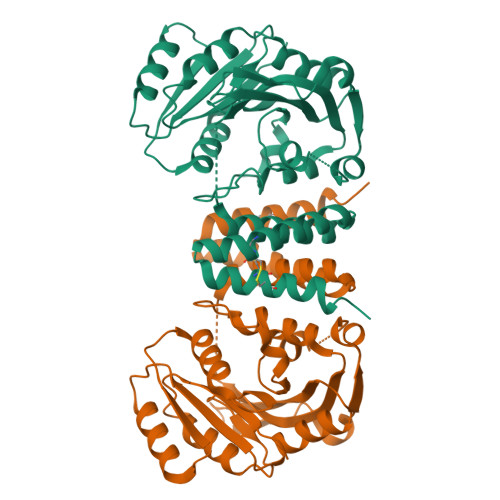
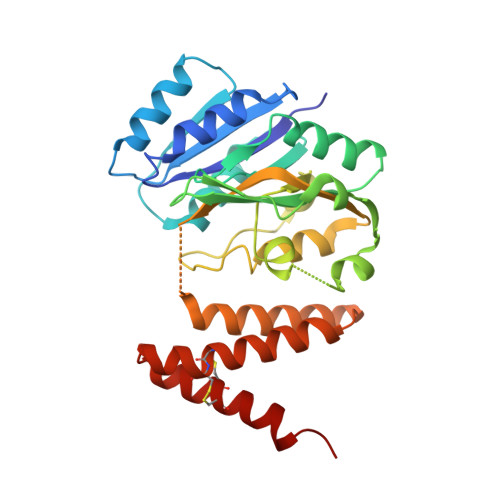
Serine-rich repeat glycoproteins (SRRPs) conserved in streptococci and staphylococci are important for bacterial colonization and pathogenesis. Fap1, a well studied SRRP is a major surface constituent of Streptococcus parasanguinis and is required for bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Biogenesis of Fap1 is a multistep process that involves both glycosylation and secretion. A series of glycosyltransferases catalyze sequential glycosylation of Fap1. We have identified a unique hybrid protein dGT1 (dual glycosyltransferase 1) that contains two distinct domains. N-terminal DUF1792 is a novel GT-D-type glycosyltransferase, transferring Glc residues to Glc-GlcNAc-modified Fap1. C-terminal dGT1 (CgT) is predicted to possess a typical GT-A-type glycosyltransferase, however, the activity remains unknown. In this study, we determine that CgT is a distinct glycosyltransferase, transferring GlcNAc residues to Glc-Glc-GlcNAc-modified Fap1. A 2.4-Å x-ray crystal structure reveals that CgT has a unique binding domain consisting of three α helices in addition to a typical GT-A-type glycosyltransferase domain. The helical domain is crucial for the oligomerization of CgT. Structural and biochemical studies revealed that the helix domain is required for the protein-protein interaction and crucial for the glycosyltransferase activity of CgT in vitro and in vivo As the helix domain presents a novel structural fold, we conclude that CgT represents a new member of GT-A-type glycosyltransferases.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Departments of Pediatric Dentistry and Microbiology, Schools of Dentistry and Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama 35294 and.