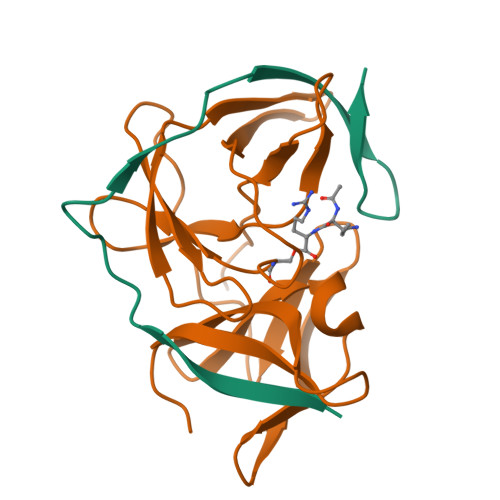
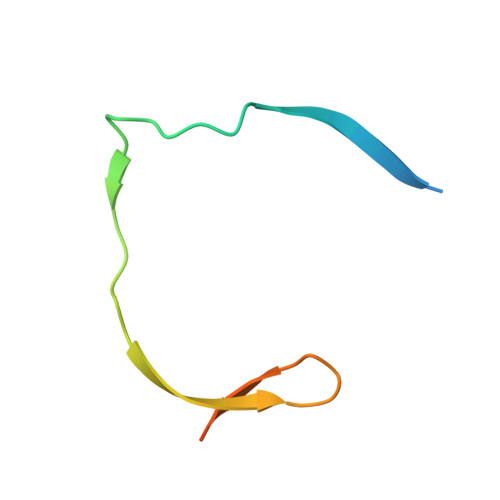
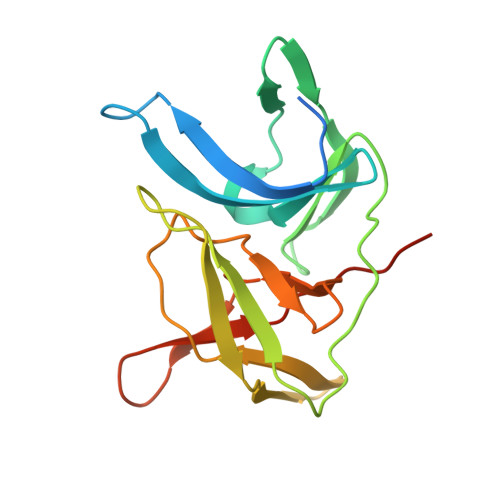
Structural Dynamics of Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease Binding to Dipeptide Inhibitors
Li, Y., Zhang, Z., Phoo, W.W., Loh, Y.R., Wang, W., Liu, S., Chen, M.W., Hung, A.W., Keller, T.H., Luo, D., Kang, C.(2017) Structure 25: 1242-1250.e3
- PubMed: 28689970
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.06.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H6V - PubMed Abstract:
The NS2B-NS3 viral protease is an attractive drug target against Zika virus (ZIKV) due to its importance in viral replication and maturation. Here we report the crystal structure of protease in complex with a dipeptide inhibitor, Acyl-KR-aldehyde (compound 1). The aldehyde moiety forms a covalent bond with the catalytic Ser 135 of NS3. The Arg and Lys residues in the inhibitor occupy the S1 and S2 sites of the protease, respectively. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies demonstrate that the complex is in the closed conformation in solution. The chemical environment of residues surrounding the active site is sensitive to the bound inhibitor as demonstrated by the comparison with two other non-covalent dipeptides, Acyl-K-Agmatine (compound 2) and Acyl-KR-COOH (compound 3). Removing the aldehyde moiety in 1 converts the binding mode from a slow to a fast exchange regime. The structural dynamics information obtained in this study will guide future drug discovery against ZIKV and other flaviviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Experimental Therapeutics Centre, Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A(∗)STAR), 31 Biopolis way, Nanos, #03-01, Singapore 138669, Singapore.