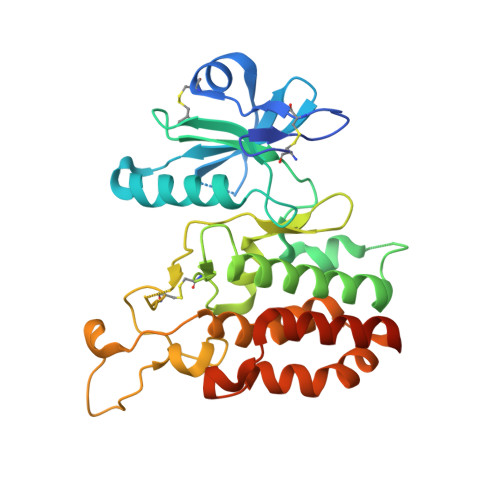
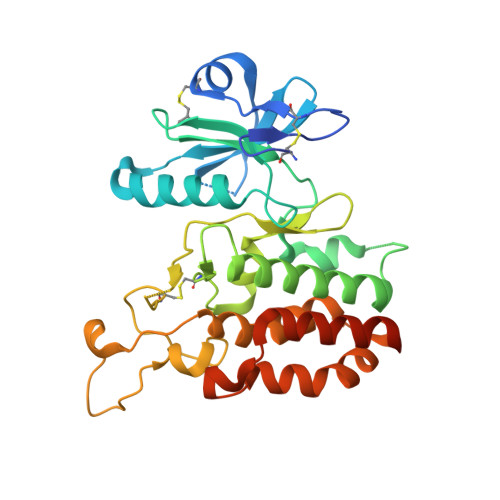
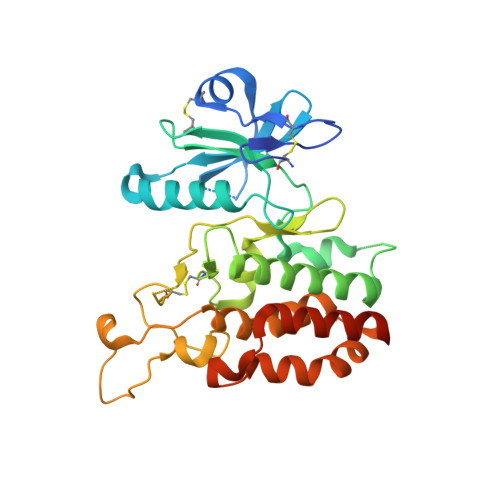
3D structural analysis of protein O-mannosyl kinase, POMK, a causative gene product of dystroglycanopathy.
Nagae, M., Mishra, S.K., Neyazaki, M., Oi, R., Ikeda, A., Matsugaki, N., Akashi, S., Manya, H., Mizuno, M., Yagi, H., Kato, K., Senda, T., Endo, T., Nogi, T., Yamaguchi, Y.(2017) Genes Cells 22: 348-359
- PubMed: 28251761
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12480
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GZ8, 5GZ9 - PubMed Abstract:
Orchestration of the multiple enzymes engaged in O-mannose glycan synthesis provides a matriglycan on α-dystroglycan (α-DG) which attracts extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as laminin. Aberrant O-mannosylation of α-DG leads to severe congenital muscular dystrophies due to detachment of ECM proteins from the basal membrane. Phosphorylation at C6-position of O-mannose catalyzed by protein O-mannosyl kinase (POMK) is a crucial step in the biosynthetic pathway of O-mannose glycan. Several mis-sense mutations of the POMK catalytic domain are known to cause a severe congenital muscular dystrophy, Walker-Warburg syndrome. Due to the low sequence similarity with other typical kinases, structure-activity relationships of this enzyme remain unclear. Here, we report the crystal structures of the POMK catalytic domain in the absence and presence of an ATP analogue and O-mannosylated glycopeptide. The POMK catalytic domain shows a typical protein kinase fold consisting of N- and C-lobes. Mannose residue binds to POMK mainly via the hydroxyl group at C2-position, differentiating from other monosaccharide residues. Intriguingly, the two amino acid residues K92 and D228, interacting with the triphosphate group of ATP, are donated from atypical positions in the primary structure. Mutations in this protein causing muscular dystrophies can now be rationalized.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Glycobiology Team, Systems Glycobiology Research Group, RIKEN-Max Planck Joint Research Center, RIKEN Global Research Cluster, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama, 351-0198, Japan.