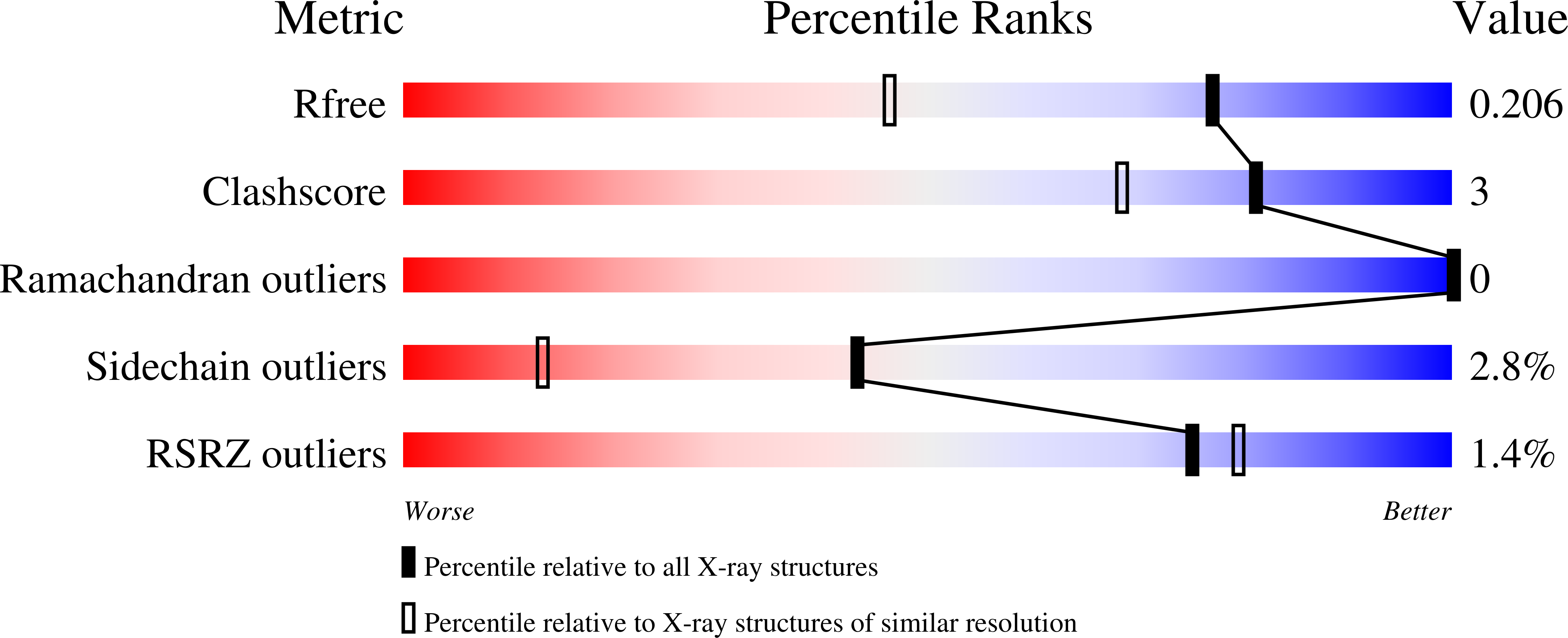
Evolutionary drivers of thermoadaptation in enzyme catalysis.
Nguyen, V., Wilson, C., Hoemberger, M., Stiller, J.B., Agafonov, R.V., Kutter, S., English, J., Theobald, D.L., Kern, D.(2017) Science 355: 289-294
- PubMed: 28008087
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah3717
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5G3Y, 5G3Z, 5G40, 5G41 - PubMed Abstract:
With early life likely to have existed in a hot environment, enzymes had to cope with an inherent drop in catalytic speed caused by lowered temperature. Here we characterize the molecular mechanisms underlying thermoadaptation of enzyme catalysis in adenylate kinase using ancestral sequence reconstruction spanning 3 billion years of evolution. We show that evolution solved the enzyme's key kinetic obstacle-how to maintain catalytic speed on a cooler Earth-by exploiting transition-state heat capacity. Tracing the evolution of enzyme activity and stability from the hot-start toward modern hyperthermophilic, mesophilic, and psychrophilic organisms illustrates active pressure versus passive drift in evolution on a molecular level, refutes the debated activity/stability trade-off, and suggests that the catalytic speed of adenylate kinase is an evolutionary driver for organismal fitness.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Biochemistry, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA 02452, USA.