Discovery of (R,E)-N-(7-Chloro-1-(1-[4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enoyl]azepan-3-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methylisonicotinamide (EGF816), a Novel, Potent, and WT Sparing Covalent Inhibitor of Oncogenic (L858R, ex19del) and Resistant (T790M) EGFR Mutants for the Treatment of EGFR Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers.
Lelais, G., Epple, R., Marsilje, T.H., Long, Y.O., McNeill, M., Chen, B., Lu, W., Anumolu, J., Badiger, S., Bursulaya, B., DiDonato, M., Fong, R., Juarez, J., Li, J., Manuia, M., Mason, D.E., Gordon, P., Groessl, T., Johnson, K., Jia, Y., Kasibhatla, S., Li, C., Isbell, J., Spraggon, G., Bender, S., Michellys, P.Y.(2016) J Med Chem 59: 6671-6689
- PubMed: 27433829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01985
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
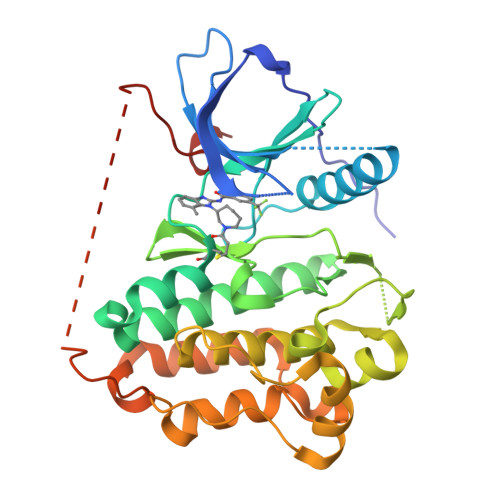
5FED, 5FEE, 5FEQ - PubMed Abstract:
Over the past decade, first and second generation EGFR inhibitors have significantly improved outcomes for lung cancer patients with activating mutations in EGFR. However, both resistance through a secondary T790M mutation at the gatekeeper residue and dose-limiting toxicities from wild-type (WT) EGFR inhibition ultimately limit the full potential of these therapies to control mutant EGFR-driven tumors and new therapies are urgently needed. Herein, we describe our approach toward the discovery of 47 (EGF816, nazartinib), a novel, covalent mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor with equipotent activity on both oncogenic and T790M-resistant EGFR mutations. Through molecular docking studies we converted a mutant-selective high-throughput screening hit (7) into a number of targeted covalent EGFR inhibitors with equipotent activity across mutants EGFR and good WT-EGFR selectivity. We used an abbreviated in vivo efficacy study for prioritizing compounds with good tolerability and efficacy that ultimately led to the selection of 47 as the clinical candidate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation , 10675 John J. Hopkins Drive, San Diego, California 92121, United States.