Structural insights into the interaction of the ribosomal P stalk protein P2 with a type II ribosome-inactivating protein ricin
Fan, X., Zhu, Y., Wang, C., Niu, L., Teng, M., Li, X.(2016) Sci Rep 6: 37803-37803
- PubMed: 27886256
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37803
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5DDZ - PubMed Abstract:
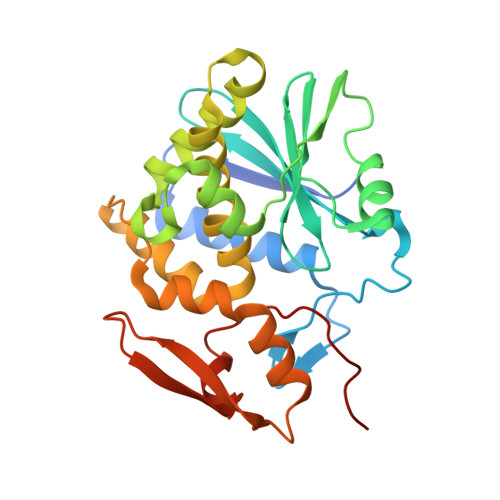
Ricin is a type II ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) that depurinates A 4324 at the sarcin-ricin loop of 28 S ribosomal RNA (rRNA), thus inactivating the ribosome by preventing elongation factors from binding to the GTPase activation centre. Recent studies have disclosed that the conserved C-terminal domain (CTD) of eukaryotic ribosomal P stalk proteins is involved in the process that RIPs target ribosome. However, the details of the molecular interaction between ricin and P stalk proteins remain unknown. Here, we report the structure of ricin-A chain (RTA) in a complex with the CTD of the human ribosomal protein P2. The structure shows that the Phe 111 , Leu 113 and Phe 114 residues of P2 insert into a hydrophobic pocket formed by the Tyr 183 , Arg 235 , Phe 240 and Ile 251 residues of RTA, while Asp 115 of P2 forms hydrogen bonds with Arg 235 of RTA. The key residues in RTA and P2 for complex formation were mutated, and their importance was determined by pull-down assays. The results from cell-free translation assays further confirmed that the interaction with P stalk proteins is essential for the inhibition of protein synthesis by RTA. Taken together, our results provide a structural basis that will improve our understanding of the process by which ricin targets the ribosome, which will benefit the development of effective small-molecule inhibitors for use as therapeutic agents.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, Innovation Center for Cell Signaling Networks, School of Life Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026, People's Republic of China.