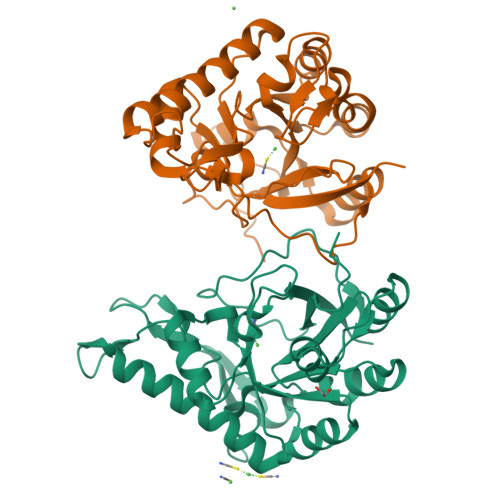
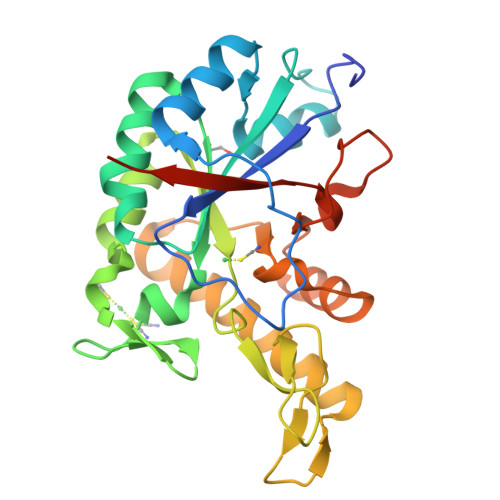
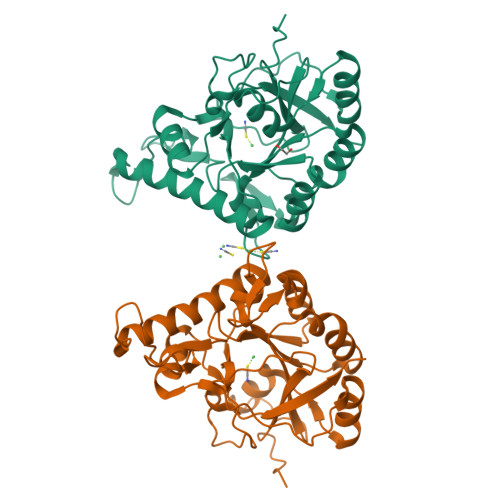
The Protein BpsB Is a Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine Deacetylase Required for Biofilm Formation in Bordetella bronchiseptica.
Little, D.J., Milek, S., Bamford, N.C., Ganguly, T., DiFrancesco, B.R., Nitz, M., Deora, R., Howell, P.L.(2015) J Biological Chem 290: 22827-22840
- PubMed: 26203190
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.672469
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5BU6 - PubMed Abstract:
Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica are the causative agents of whooping cough in humans and a variety of respiratory diseases in animals, respectively. Bordetella species produce an exopolysaccharide, known as the Bordetella polysaccharide (Bps), which is encoded by the bpsABCD operon. Bps is required for Bordetella biofilm formation, colonization of the respiratory tract, and confers protection from complement-mediated killing. In this report, we have investigated the role of BpsB in the biosynthesis of Bps and biofilm formation by B. bronchiseptica. BpsB is a two-domain protein that localizes to the periplasm and outer membrane. BpsB displays metal- and length-dependent deacetylation on poly-β-1,6-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (PNAG) oligomers, supporting previous immunogenic data that suggests Bps is a PNAG polymer. BpsB can use a variety of divalent metal cations for deacetylase activity and showed highest activity in the presence of Ni(2+) and Co(2+). The structure of the BpsB deacetylase domain is similar to the PNAG deacetylases PgaB and IcaB and contains the same circularly permuted family four carbohydrate esterase motifs. Unlike PgaB from Escherichia coli, BpsB is not required for polymer export and has unique structural differences that allow the N-terminal deacetylase domain to be active when purified in isolation from the C-terminal domain. Our enzymatic characterizations highlight the importance of conserved active site residues in PNAG deacetylation and demonstrate that the C-terminal domain is required for maximal deacetylation of longer PNAG oligomers. Furthermore, we show that BpsB is critical for the formation and complex architecture of B. bronchiseptica biofilms.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Program in Molecular Structure and Function, Research Institute, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario M5G 1X8, the Department of Biochemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5S 1A8, Canada.