Structural and Mutagenic Analysis of Metallo-beta-Lactamase IMP-18
Furuyama, T., Nonomura, H., Ishii, Y., Hanson, N.D., Shimizu-Ibuka, A.(2016) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60: 5521-5526
- PubMed: 27381398
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00985-16
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5B3R - PubMed Abstract:
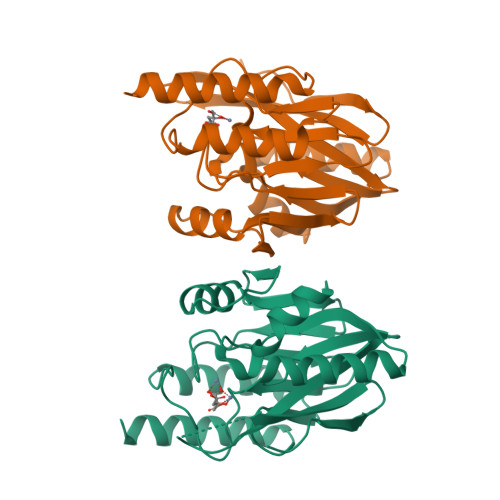
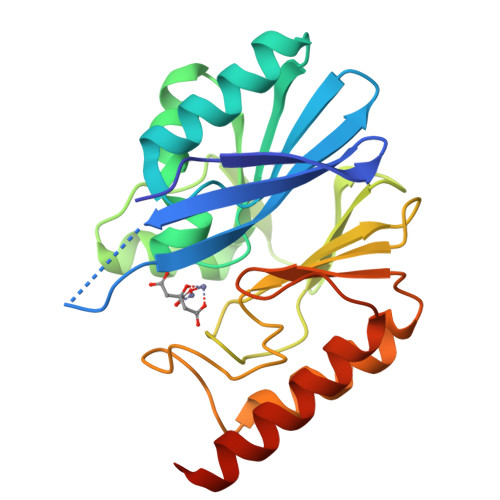
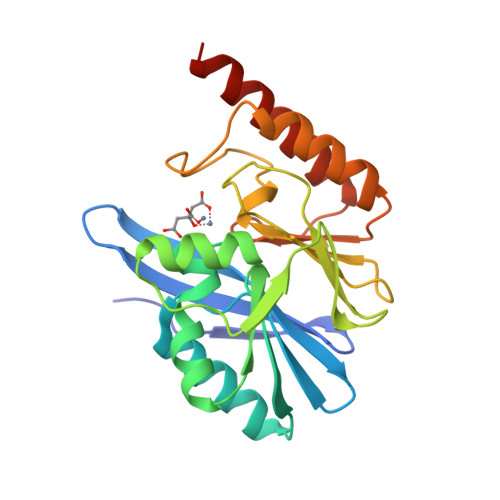
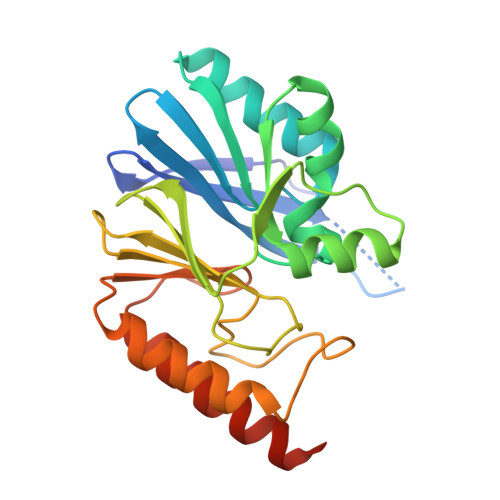
IMP-type metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) are exogenous zinc metalloenzymes that hydrolyze a broad range of β-lactams, including carbapenems. Here we report the crystal structure of IMP-18, an MBL cloned from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, at 2.0-Å resolution. The overall structure of IMP-18 resembles that of IMP-1, with an αβ/βα "folded sandwich" configuration, but the loop that covers the active site has a distinct conformation. The relationship between IMP-18's loop conformation and its kinetic properties was investigated by replacing the amino acid residues that can affect the loop conformation (Lys44, Thr50, and Ile69) in IMP-18 with those occupying the corresponding positions in the well-described enzyme IMP-1. The replacement of Thr50 with Pro considerably modified IMP-18's kinetic properties, specifically those pertaining to meropenem, with the kcat/Km value increased by an order of magnitude. The results indicate that this is a key residue that defines the kinetic properties of IMP-type β-lactamases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Material and Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Yamagata University, Yamagata, Japan.