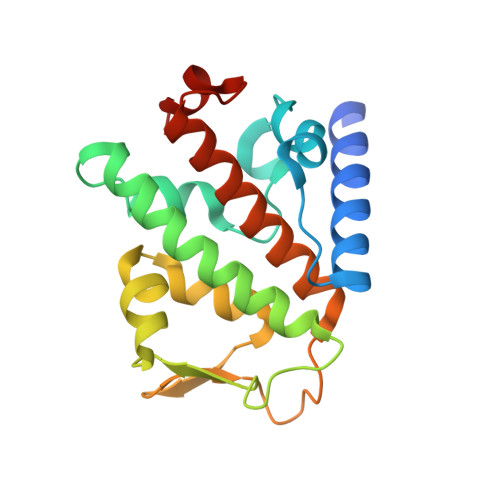
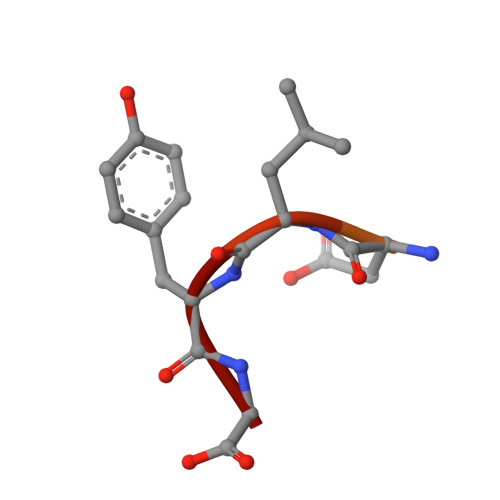
Binding of OTULIN to the PUB domain of HOIP controls NF-kappa B signaling.
Schaeffer, V., Akutsu, M., Olma, M.H., Gomes, L.C., Kawasaki, M., Dikic, I.(2014) Mol Cell 54: 349-361
- PubMed: 24726327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4P09, 4P0A, 4P0B - PubMed Abstract:
Linear ubiquitin chains are implicated in the regulation of the NF-κB pathway, immunity, and inflammation. They are synthesized by the LUBAC complex containing the catalytic subunit HOIL-1-interacting protein (HOIP) and are disassembled by the linear ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinase OTULIN. Little is known about the regulation of these opposing activities. Here we demonstrate that HOIP and OTULIN interact and act as a bimolecular editing pair for linear ubiquitin signals in vivo. The HOIP PUB domain binds to the PUB interacting motif (PIM) of OTULIN and the chaperone VCP/p97. Structural studies revealed the basis of high-affinity interaction with the OTULIN PIM. The conserved Tyr56 of OTULIN makes critical contacts with the HOIP PUB domain, and its phosphorylation negatively regulates this interaction. Functionally, HOIP binding to OTULIN is required for the recruitment of OTULIN to the TNF receptor complex and to counteract HOIP-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway.
- Institute of Biochemistry II, Goethe University Faculty of Medicine, 60590 Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: