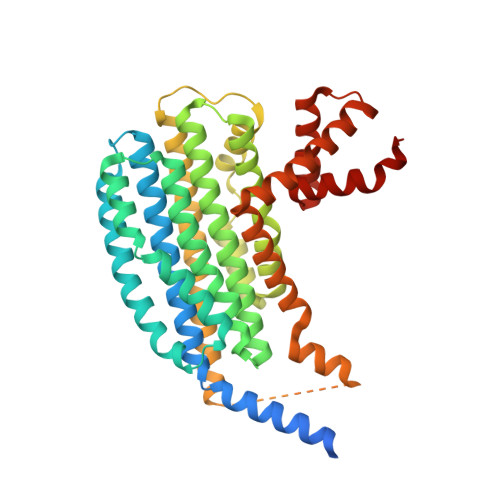
The Structure of the Nasr Transcription Antiterminator Reveals a One-Component System with a Nit Nitrate Receptor Coupled to an Antar RNA-Binding Effector.
Boudes, M., Lazar, N., Graille, M., Durand, D., Gaidenko, T.A., Stewart, V., Van Tilbeurgh, H.(2012) Mol Microbiol 85: 431
- PubMed: 22690729
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08111.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AKK - PubMed Abstract:
The nitrate- and nitrite-sensing NIT domain is present in diverse signal-transduction proteins across a wide range of bacterial species. NIT domain function was established through analysis of the Klebsiella oxytoca NasR protein, which controls expression of the nasF operon encoding enzymes for nitrite and nitrate assimilation. In the presence of nitrate or nitrite, the NasR protein inhibits transcription termination at the factor-independent terminator site in the nasF operon transcribed leader region. We present here the crystal structure of the intact NasR protein in the apo state. The dimeric all-helical protein contains a large amino-terminal NIT domain that associates two four-helix bundles, and a carboxyl-terminal ANTAR (AmiR and NasR transcription antitermination regulator) domain. The analysis reveals unexpectedly that the NIT domain is structurally similar to the periplasmic input domain of the NarX two-component sensor that regulates nitrate and nitrite respiration. This similarity suggests that the NIT domain binds nitrate and nitrite between two invariant arginyl residues located on adjacent alpha helices, and results from site-specific mutagenesis showed that these residues are critical for NasR function. The resulting structural movements in the NIT domain would provoke an active configuration of the ANTAR domains necessary for specific leader mRNA binding.
- IBBMC-CNRS UMR8619, Bât. 430, Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay, France.
Organizational Affiliation: