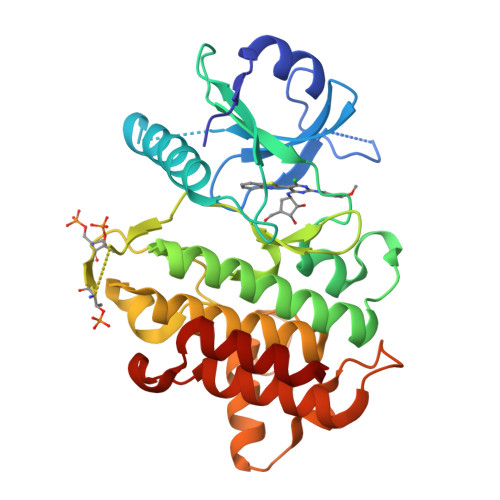
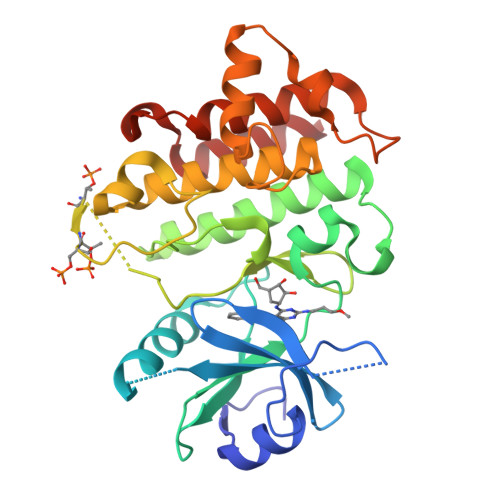
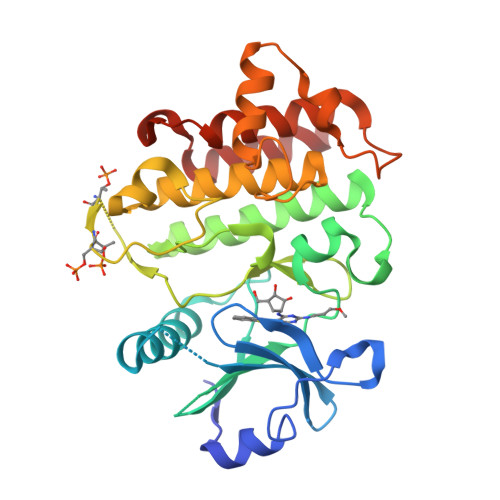
Discovery and hit-to-lead optimization of 2,6-diaminopyrimidine inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4.
McElroy, W.T., Michael Seganish, W., Jason Herr, R., Harding, J., Yang, J., Yet, L., Komanduri, V., Prakash, K.C., Lavey, B., Tulshian, D., Greenlee, W.J., Sondey, C., Fischmann, T.O., Niu, X.(2015) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 1836-1841
- PubMed: 25870132
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.03.043
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XS2 - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is a critical element of the Toll-like/interleukin-1 receptor inflammation signaling pathway. A screening campaign identified a novel diaminopyrimidine hit that exhibits weak IRAK4 inhibitory activity and a ligand efficiency of 0.25. Hit-to-lead activities were conducted through independent SAR studies of each of the four pyrimidine substituents. Optimal activity was observed upon removal of the pyrimidine C-4 chloro substituent. The intact C-6 carboribose is required for IRAK4 inhibition. Numerous heteroaryls were tolerated at the C-5 position, with azabenzothiazoles conferring the best activities. Aminoheteroaryls were preferred at the C-2 position. These studies led to the discovery of inhibitors 35, 36, and 38 that exhibit nanomolar inhibition of IRAK4, improved ligand efficiencies, and modest kinase selectivities.
Organizational Affiliation:
Discovery Chemistry, Merck Research Laboratories, 2015 Galloping Hill Rd., Kenilworth, NJ 07033, United States. Electronic address: william.mcelroy@merck.com.