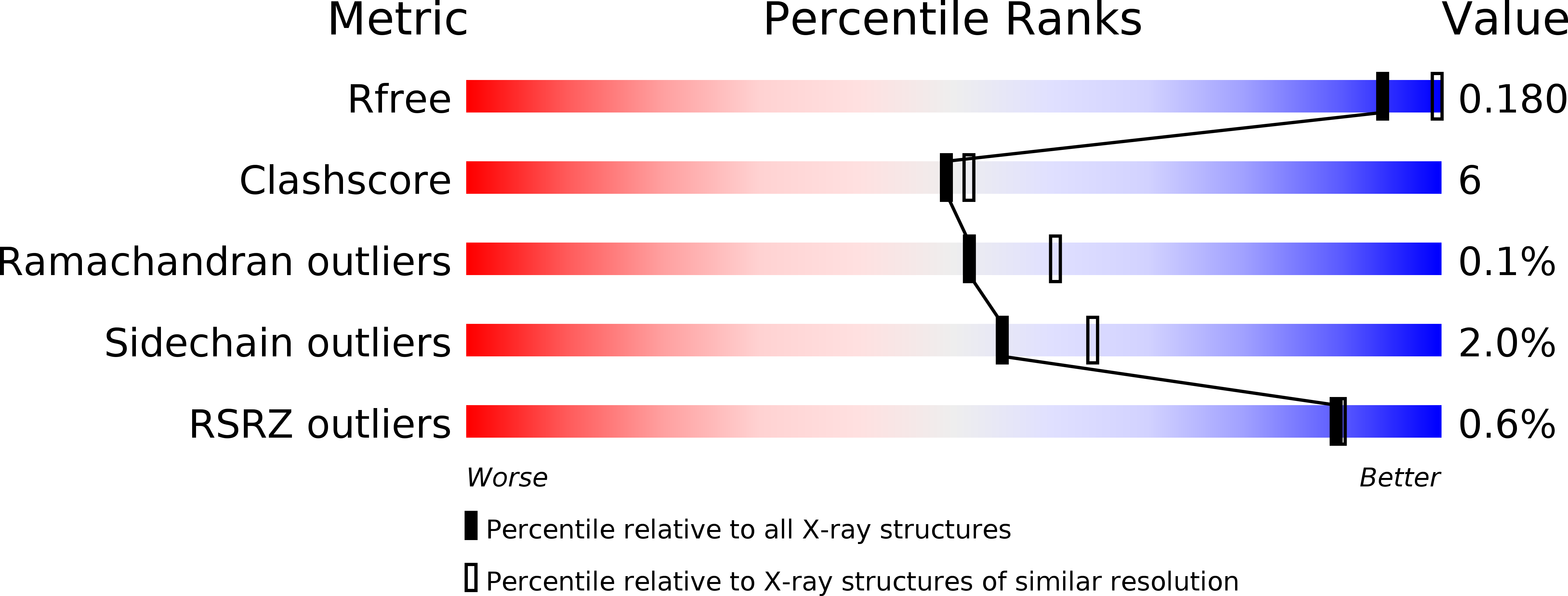
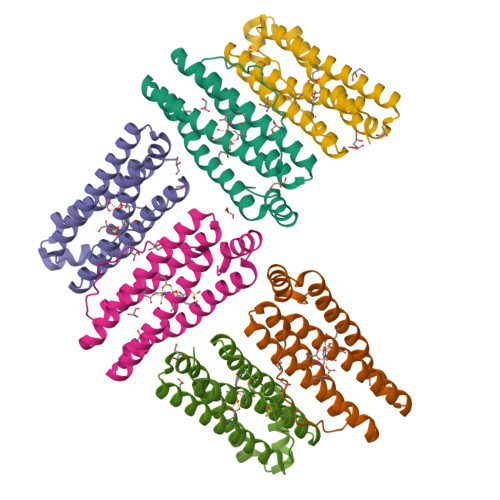
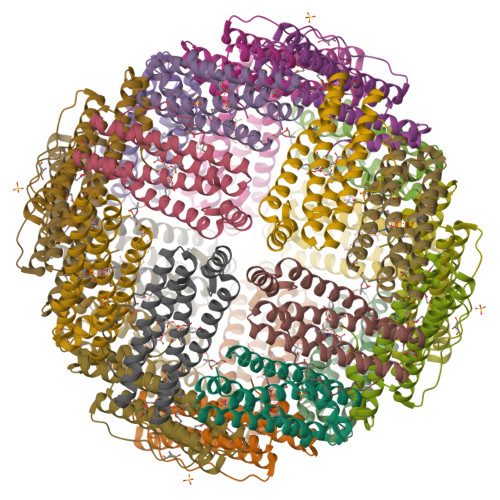
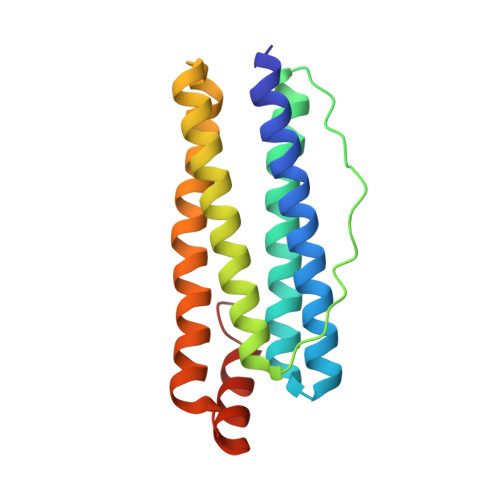
Structural Basis of Novel Iron-Uptake Route and Reaction Intermediates in Ferritins from Gram-Negative Bacteria
Kim, S., Lee, J.H., Seok, J.H., Park, Y.H., Jung, S.W., Cho, A.E., Lee, C., Chung, M.S., Kim, K.H.(2016) J Mol Biology 428: 5007-5018
- PubMed: 27777002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.10.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XGS, 4ZTT, 5C6F - PubMed Abstract:
Iron and oxygen chemistry is mediated by iron proteins for many biological functions. Carboxylate-bridged diiron enzymes including ferritin have the common mechanism of oxygen activation via peroxodiferric intermediates. However, the route for iron uptake and the structural identification of intermediates still remain incomplete. The 4-fold symmetry channel of Helicobacter pylori ferritin was previously proposed as the iron-uptake route in eubacteria, but the amino acid residues at the 4-fold channel are not highly conserved. Here, we show evidence for a short path for iron uptake from His93 on the surface to the ferroxidase center in H. pylori ferritin and Escherichia coli ferritin. The amino acid residues along this path are highly conserved in Gram-negative bacteria and some archaea, and the mutants containing S20A and H93L showed significantly decreased iron oxidation. Surprisingly, the E. coli ferritin S20A crystal structure showed oxygen binding and side-on, symmetric μ-η 2 :η 2 peroxodiferric and oxodiferric intermediates. The results provide the structural basis for understanding the chemical nature of intermediates in iron oxidation in bacteria and some of archaea.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotechnology & Bioinformatics, Korea University, Sejong 339-700, Korea.