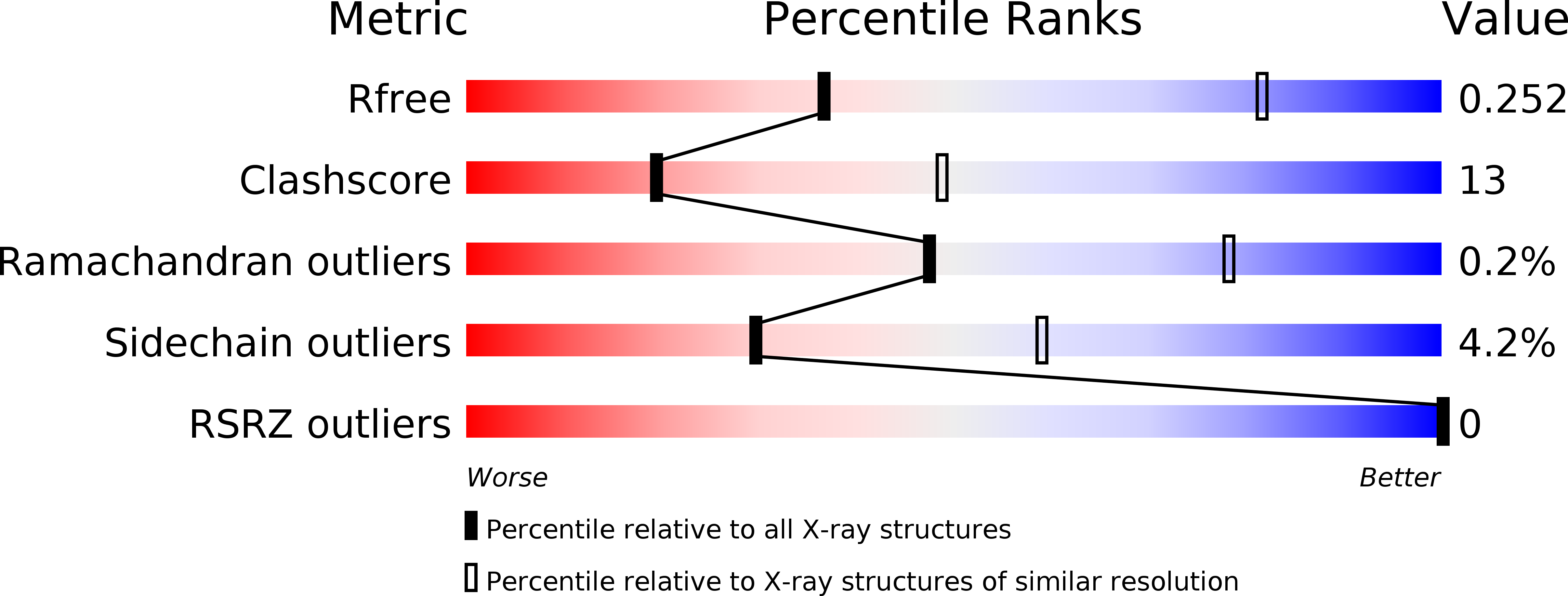
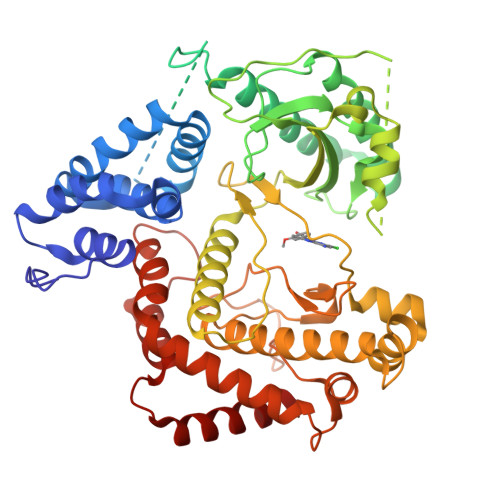
Highly Selective Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase III beta Inhibitors and Structural Insight into Their Mode of Action.
Mejdrova, I., Chalupska, D., Kogler, M., Sala, M., Plackova, P., Baumlova, A., Hrebabecky, H., Prochazkova, E., Dejmek, M., Guillon, R., Strunin, D., Weber, J., Lee, G., Birkus, G., Mertlikova-Kaiserova, H., Boura, E., Nencka, R.(2015) J Med Chem 58: 3767-3793
- PubMed: 25897704
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00499
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WAE, 4WAG - PubMed Abstract:
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIβ is a cellular lipid kinase pivotal to pathogenesis of various RNA viruses. These viruses hijack the enzyme in order to modify the structure of intracellular membranes and use them for the construction of functional replication machinery. Selective inhibitors of this enzyme are potential broad-spectrum antiviral agents, as inhibition of this enzyme results in the arrest of replication of PI4K IIIβ-dependent viruses. Herein, we report a detailed study of novel selective inhibitors of PI4K IIIβ, which exert antiviral activity against a panel of single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses. Our crystallographic data show that the inhibitors occupy the binding site for the adenine ring of the ATP molecule and therefore prevent the phosphorylation reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
‡Gilead Sciences, Inc., 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, California 94404, United States.