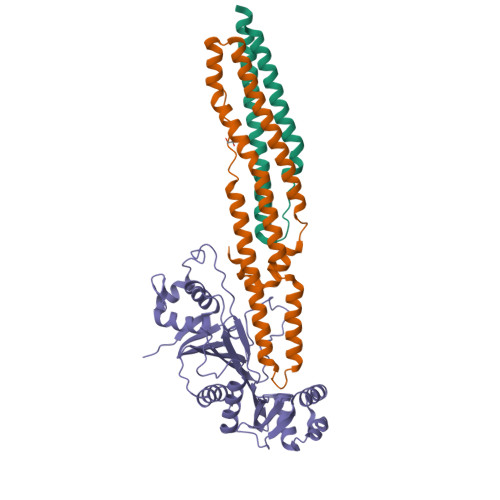
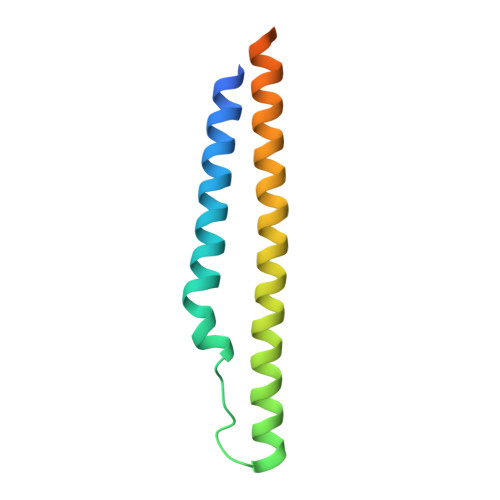
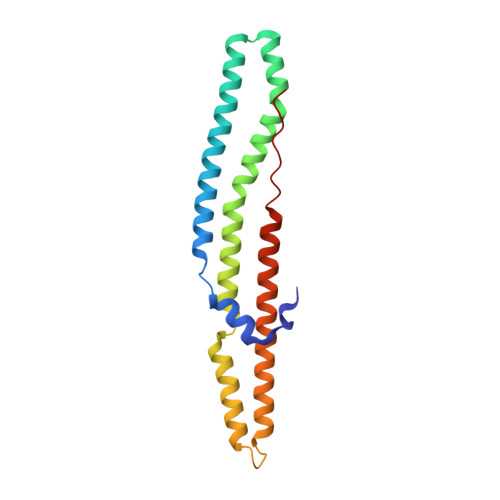
Structure of a PE-PPE-EspG complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals molecular specificity of ESX protein secretion.
Ekiert, D.C., Cox, J.S.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 14758-14763
- PubMed: 25275011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1409345111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4W4I, 4W4J, 4W4K, 4W4L - PubMed Abstract:
Nearly 10% of the coding capacity of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome is devoted to two highly expanded and enigmatic protein families called PE and PPE, some of which are important virulence/immunogenicity factors and are secreted during infection via a unique alternative secretory system termed "type VII." How PE-PPE proteins function during infection and how they are translocated to the bacterial surface through the five distinct type VII secretion systems [ESAT-6 secretion system (ESX)] of M. tuberculosis is poorly understood. Here, we report the crystal structure of a PE-PPE heterodimer bound to ESX secretion-associated protein G (EspG), which adopts a novel fold. This PE-PPE-EspG complex, along with structures of two additional EspGs, suggests that EspG acts as an adaptor that recognizes specific PE-PPE protein complexes via extensive interactions with PPE domains, and delivers them to ESX machinery for secretion. Surprisingly, secretion of most PE-PPE proteins in M. tuberculosis is likely mediated by EspG from the ESX-5 system, underscoring the importance of ESX-5 in mycobacterial pathogenesis. Moreover, our results indicate that PE-PPE domains function as cis-acting targeting sequences that are read out by EspGs, revealing the molecular specificity for secretion through distinct ESX pathways.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of California, San Francisco, CA 94143 damian.ekiert@ucsf.edu jeffery.cox@ucsf.edu.