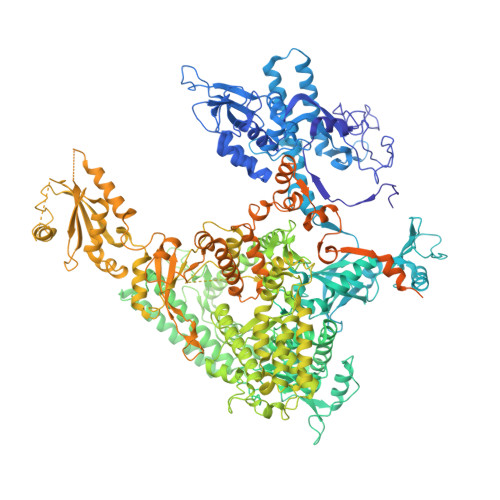
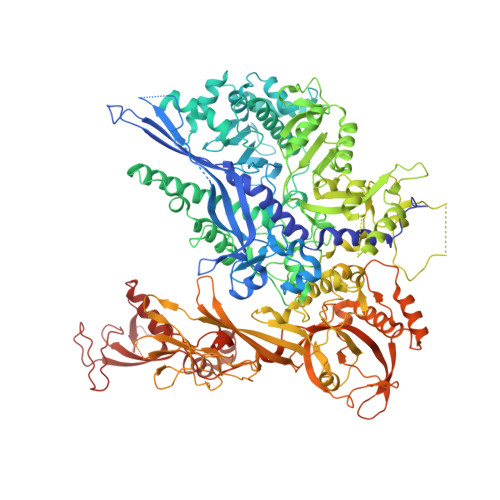
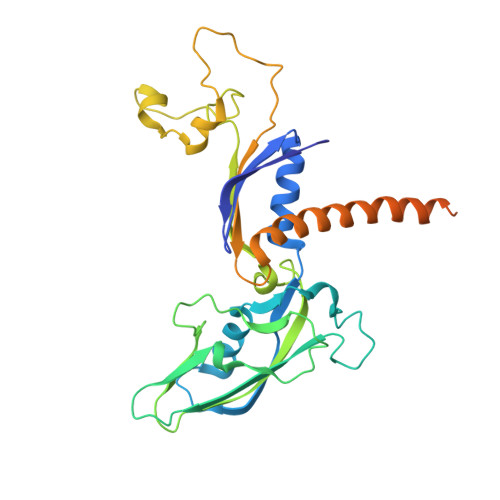
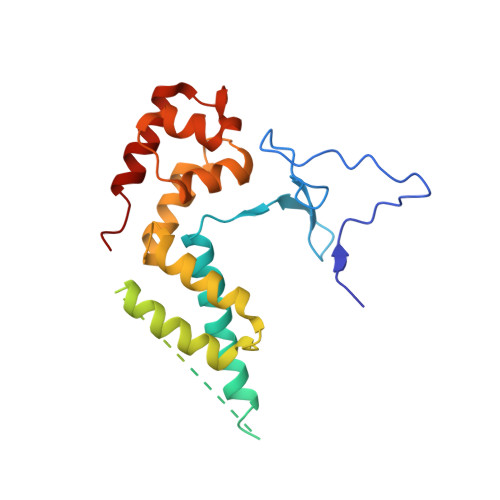
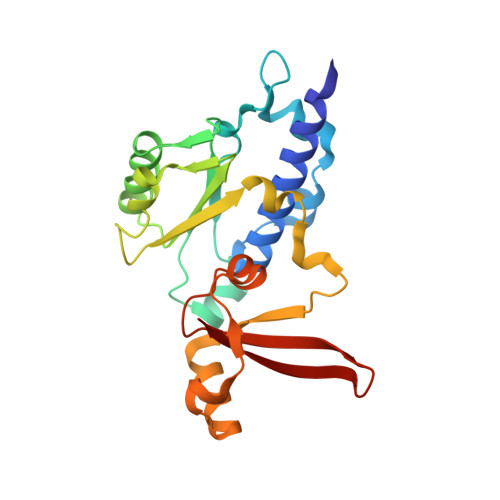
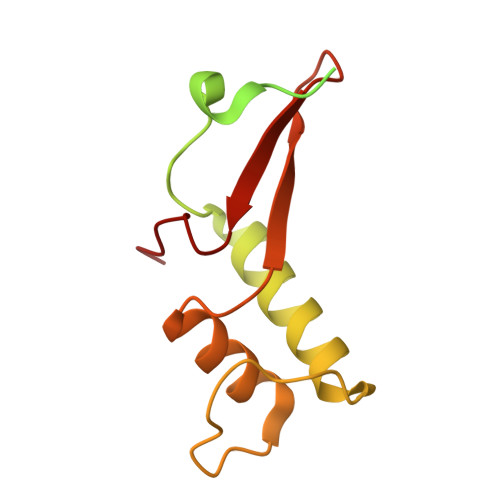
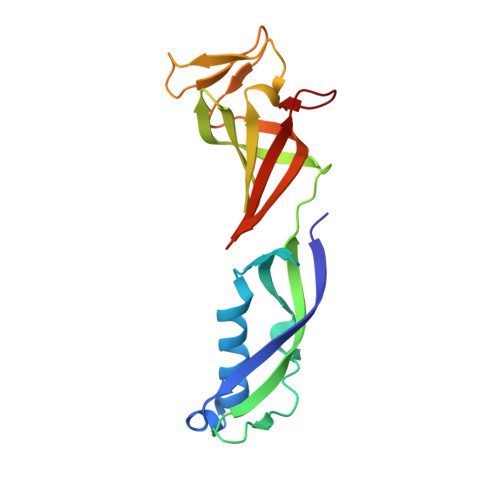
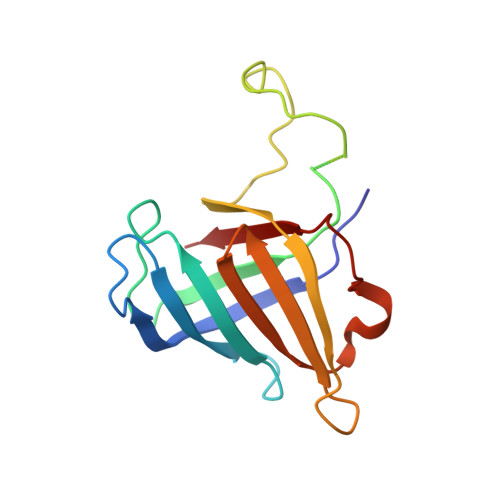
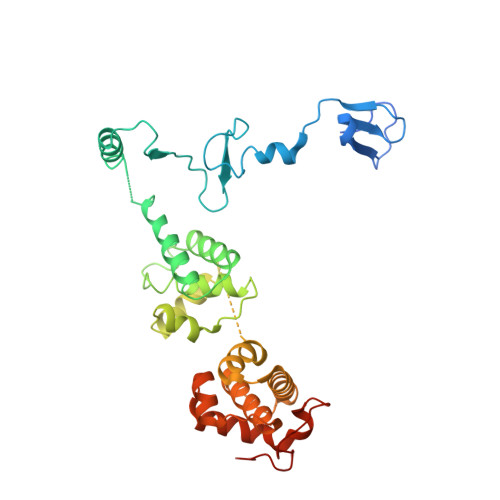
Architecture of the RNA Polymerase II-Mediator Core Initiation Complex.
Plaschka, C., Lariviere, L., Wenzeck, L., Seizl, M., Hemann, M., Tegunov, D., Petrotchenko, E.V., Borchers, C.H., Baumeister, W., Herzog, F., Villa, E., Cramer, P.(2015) Nature 518: 376
- PubMed: 25652824
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14229
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4V1M, 4V1N, 4V1O - PubMed Abstract:
The conserved co-activator complex Mediator enables regulated transcription initiation by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Here we reconstitute an active 15-subunit core Mediator (cMed) comprising all essential Mediator subunits from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The cryo-electron microscopic structure of cMed bound to a core initiation complex was determined at 9.7 Å resolution. cMed binds Pol II around the Rpb4-Rpb7 stalk near the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD). The Mediator head module binds the Pol II dock and the TFIIB ribbon and stabilizes the initiation complex. The Mediator middle module extends to the Pol II foot with a 'plank' that may influence polymerase conformation. The Mediator subunit Med14 forms a 'beam' between the head and middle modules and connects to the tail module that is predicted to bind transcription activators located on upstream DNA. The Mediator 'arm' and 'hook' domains contribute to a 'cradle' that may position the CTD and TFIIH kinase to stimulate Pol II phosphorylation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Molecular Biology, Am Fassberg 11, 37077 Göttingen, Germany.