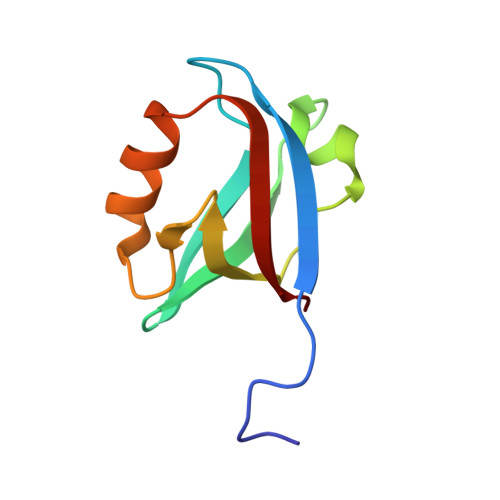
Structures of the human Pals1 PDZ domain with and without ligand suggest gated access of Crb to the PDZ peptide-binding groove.
Ivanova, M.E., Fletcher, G.C., O'Reilly, N., Purkiss, A.G., Thompson, B.J., McDonald, N.Q.(2015) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71: 555-564
- PubMed: 25760605
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S139900471402776X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UU5, 4UU6 - PubMed Abstract:
Many components of epithelial polarity protein complexes possess PDZ domains that are required for protein interaction and recruitment to the apical plasma membrane. Apical localization of the Crumbs (Crb) transmembrane protein requires a PDZ-mediated interaction with Pals1 (protein-associated with Lin7, Stardust, MPP5), a member of the p55 family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs). This study describes the molecular interaction between the Crb carboxy-terminal motif (ERLI), which is required for Drosophila cell polarity, and the Pals1 PDZ domain using crystallography and fluorescence polarization. Only the last four Crb residues contribute to Pals1 PDZ-domain binding affinity, with specificity contributed by conserved charged interactions. Comparison of the Crb-bound Pals1 PDZ structure with an apo Pals1 structure reveals a key Phe side chain that gates access to the PDZ peptide-binding groove. Removal of this side chain enhances the binding affinity by more than fivefold, suggesting that access of Crb to Pals1 may be regulated by intradomain contacts or by protein-protein interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratories, Cancer Research UK, 44 Lincoln's Inn Fields, London WC2A 3LY, England.