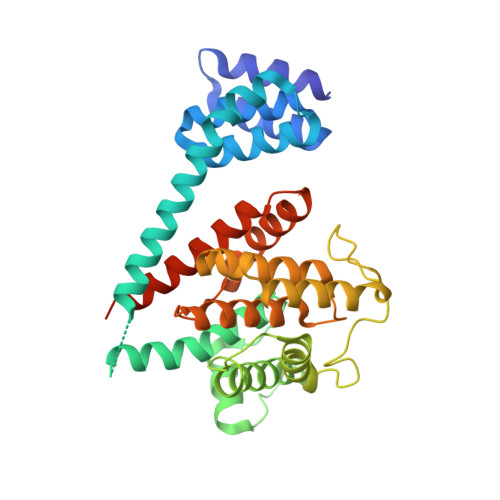
Crystal structure of the human, FIC-domain containing protein HYPE and implications for its functions.
Bunney, T.D., Cole, A.R., Broncel, M., Esposito, D., Tate, E.W., Katan, M.(2014) Structure 22: 1831-1843
- PubMed: 25435325
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.10.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4U04, 4U07, 4U0S, 4U0U, 4U0Z - PubMed Abstract:
Protein AMPylation, the transfer of AMP from ATP to protein targets, has been recognized as a new mechanism of host-cell disruption by some bacterial effectors that typically contain a FIC-domain. Eukaryotic genomes also encode one FIC-domain protein,HYPE, which has remained poorly characterized.Here we describe the structure of human HYPE, solved by X-ray crystallography, representing the first structure of a eukaryotic FIC-domain protein. We demonstrate that HYPE forms stable dimers with structurally and functionally integrated FIC-domains and with TPR-motifs exposed for protein-protein interactions. As HYPE also uniquely possesses a transmembrane helix, dimerization is likely to affect its positioning and function in the membrane vicinity. The low rate of auto AMPylation of the wild-type HYPE could be due to autoinhibition, consistent with the mechanism proposed for a number of putative FIC AMPylators. Our findings also provide a basis to further consider possible alternative cofactors of HYPE and distinct modes of target-recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biosciences, Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK. Electronic address: t.bunney@ucl.ac.uk.