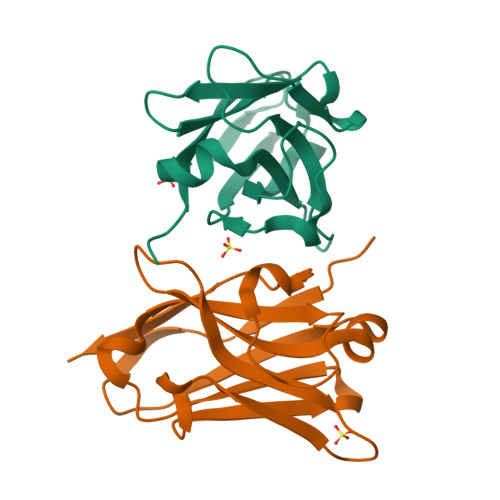
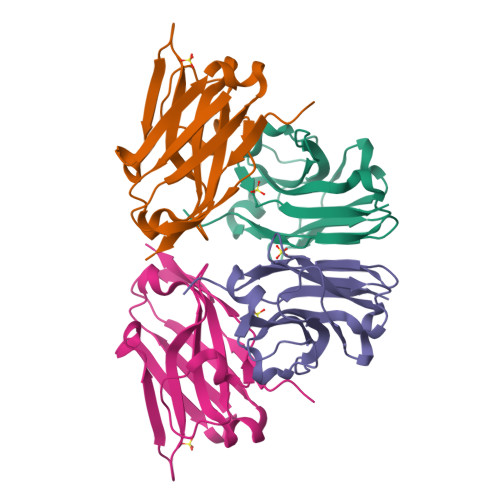
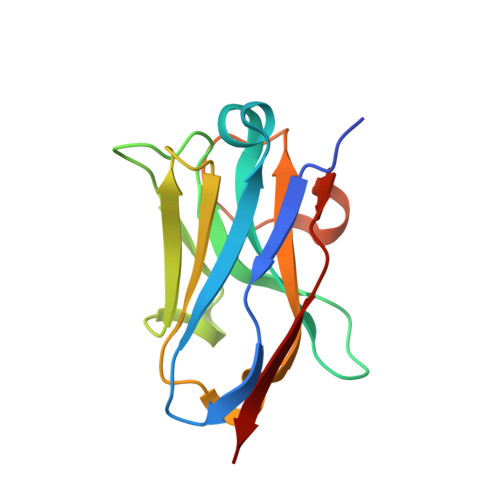
Structural and mutational analysis of a monomeric and dimeric form of a single domain antibody with implications for protein misfolding.
George, J., Compton, J.R., Leary, D.H., Olson, M.A., Legler, P.M.(2014) Proteins 82: 3101-3116
- PubMed: 25136772
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24671
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4TYU, 4U05, 4U7S, 4W68, 4W70, 4W81 - PubMed Abstract:
Camelid single domain antibodies (sdAb) are known for their thermal stability and reversible refolding. We have characterized an unusually stable sdAb recognizing Staphylococcal enterotoxin B with one of the highest reported melting temperatures (T(m) = 85°C). Unexpectedly, ∼10-20% of the protein formed a dimer in solution. Three other cases where <20% of the sdAb dimerized have been reported; however, this is the first report of both the monomeric and dimeric X-ray crystal structures. Concentration of the monomer did not lead to the formation of new dimer suggesting a stable conformationally distinct species in a fraction of the cytoplasmically expressed protein. Comparison of periplasmic and cytoplasmic expression showed that the dimer was associated with cytoplasmic expression. The disulfide bond was partially reduced in the WT protein purified from the cytoplasm and the protein irreversibly unfolded. Periplasmic expression produced monomeric protein with a fully formed disulfide bond and mostly reversible refolding. Crystallization of a disulfide-bond free variant, C22A/C99V, purified from the periplasm yielded a structure of a monomeric form, while crystallization of C22A/C99V from the cytoplasm produced an asymmetric dimer. In the dimer, a significant conformational asymmetry was found in the loop residues of the edge β-strands (S50-Y60) containing the highly variable complementarity determining region, CDR2. Two dimeric assemblies were predicted from the crystal packing. Mutation of a residue at one of the interfaces, Y98A, disrupted the dimer in solution. The pleomorphic homodimer may yield insight into the stability of misfolded states and the importance of the conserved disulfide bond in preventing their formation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Bowie State University, Bowie, 14000 Jericho Park Road, Maryland, 20715-9465.