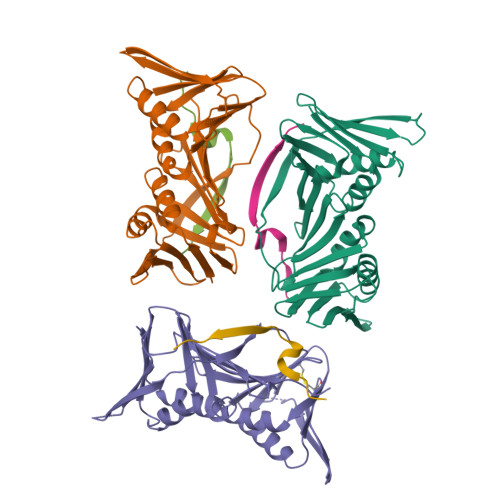
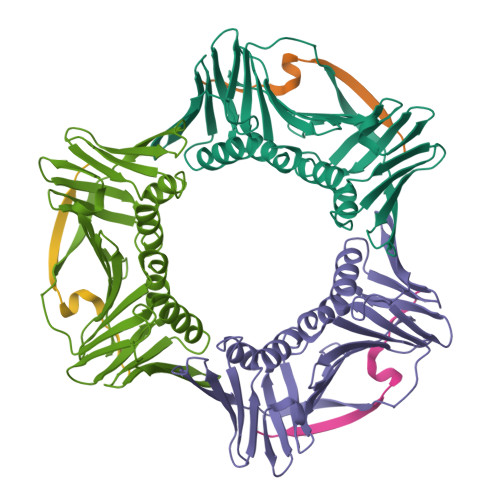
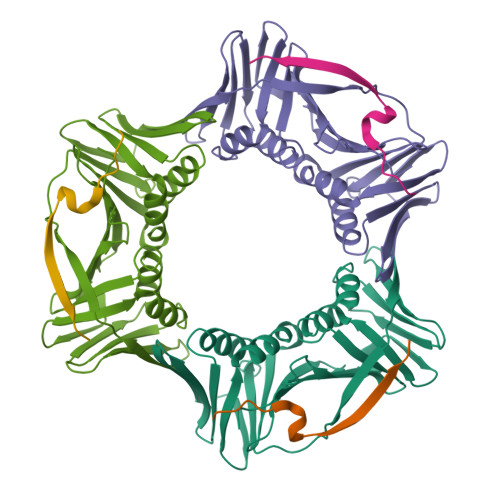
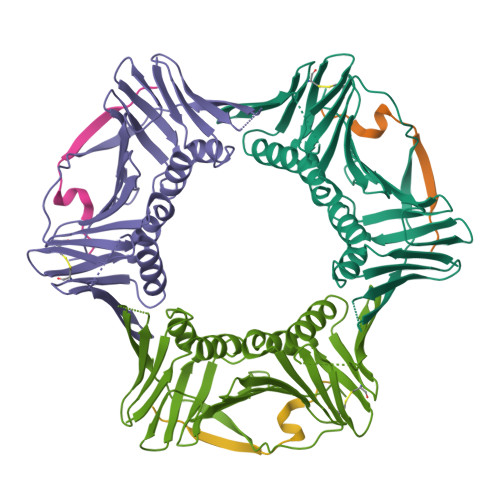
p21 Exploits Residue Tyr151 as a Tether for High-Affinity PCNA Binding.
Kroker, A.J., Bruning, J.B.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 3483-3493
- PubMed: 25972089
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00241
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4RJF - PubMed Abstract:
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA, processivity factor, sliding clamp) is a ring-shaped protein that tethers proteins to DNA in processes, including DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell-cycle control. Often used as a marker for cell proliferation, PCNA is overexpressed in cancer cells, making it an appealing pharmaceutical target. PCNA interacts with proteins through a PCNA interacting protein (PIP)-box, an eight-amino acid consensus sequence; different binding partners display a wide range of affinities based on function. Of all biological PIP-boxes, p21 has the highest known affinity for PCNA, allowing for inhibition of DNA replication and cell growth under cellular stress. As p21 is one of the few PIP-box sequences to contain a tyrosine rather than a phenylalanine in the eighth conserved position, we probed the significance of the hydroxyl group at this position using a mutational approach. Here we present the cocrystal structure of PCNA bound to a mutant p21 PIP-box peptide, p21Tyr151Phe, with associated isothermal titration calorimetry data. The p21Tyr151Phe peptide showed a 3-fold difference in affinity, as well as differences in entropy and enthalpy of binding. These differences can be attributed to a loss of hydrogen bonding capacity, as well as structural plasticity in the PCNA interdomain connector loop and the hydrophobic cavity of PCNA to which p21 binds. Thus, the hydroxyl group of Tyr151 in p21 acts as a tethering point for ideal packing and surface recognition of the peptide interface, increasing the binding affinity of p21 for PCNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, South Australia 5005, Australia.