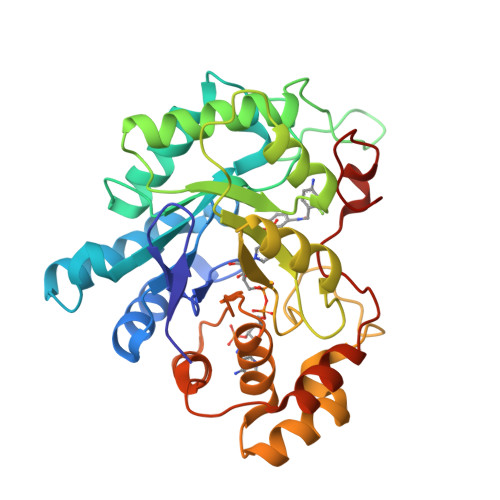
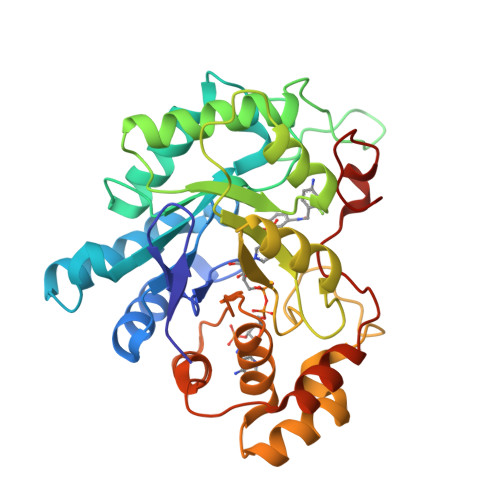
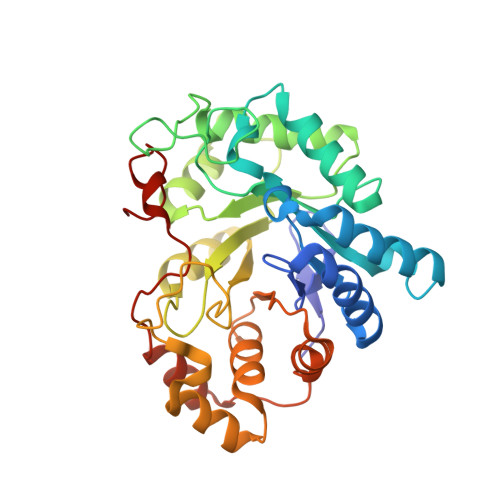
The Effect of Halogen-to-Hydrogen Bond Substitution on Human Aldose Reductase Inhibition.
Fanfrlik, J., Ruiz, F.X., Kadlcikova, A., Rezac, J., Cousido-Siah, A., Mitschler, A., Haldar, S., Lepsik, M., Kolar, M.H., Majer, P., Podjarny, A.D., Hobza, P.(2015) ACS Chem Biol 10: 1637-1642
- PubMed: 25919404
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00151
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QXI - PubMed Abstract:
The effect of halogen-to-hydrogen bond substitution on the binding energetics and biological activity of a human aldose reductase inhibitor has been studied using X-ray crystallography, IC50 measurements, advanced binding free energy calculations, and simulations. The replacement of Br or I atoms by an amine (NH2) group has not induced changes in the original geometry of the complex, which made it possible to study the isolated features of selected noncovalent interactions in a biomolecular complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
†Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry (IOCB) and Gilead Science and IOCB Research Center, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Flemingovo nám. 2, 166 10 Prague 6, Czech Republic.