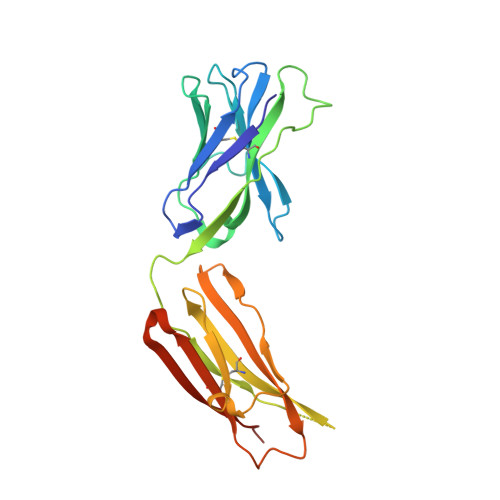
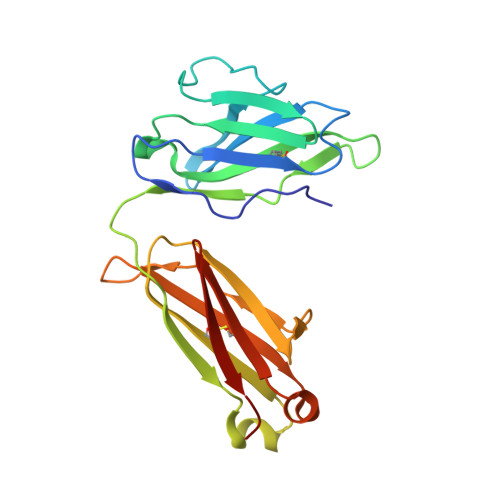
Affinity maturation in an HIV broadly neutralizing B-cell lineage through reorientation of variable domains.
Fera, D., Schmidt, A.G., Haynes, B.F., Gao, F., Liao, H.X., Kepler, T.B., Harrison, S.C.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 10275-10280
- PubMed: 24982157
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1409954111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QHK, 4QHL, 4QHM, 4QHN - PubMed Abstract:
Rapidly evolving pathogens, such as human immunodeficiency and influenza viruses, escape immune defenses provided by most vaccine-induced antibodies. Proposed strategies to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies require a deeper understanding of antibody affinity maturation and evolution of the immune response to vaccination or infection. In HIV-infected individuals, viruses and B cells evolve together, creating a virus-antibody "arms race." Analysis of samples from an individual designated CH505 has illustrated the interplay between an antibody lineage, CH103, and autologous viruses at various time points. The CH103 antibodies, relatively broad in their neutralization spectrum, interact with the CD4 binding site of gp120, with a contact dominated by CDRH3. We show by analyzing structures of progenitor and intermediate antibodies and by correlating them with measurements of binding to various gp120s that there was a shift in the relative orientation of the light- and heavy-chain variable domains during evolution of the CH103 lineage. We further show that mutations leading to this conformational shift probably occurred in response to insertions in variable loop 5 (V5) of the HIV envelope. The shift displaced the tips of the light chain away from contact with V5, making room for the inserted residues, which had allowed escape from neutralization by the progenitor antibody. These results, which document the selective mechanism underlying this example of a virus-antibody arms race, illustrate the functional significance of affinity maturation by mutation outside the complementarity determining region surface of the antibody molecule.
- Laboratory of Molecular Medicine and.
Organizational Affiliation: