High-resolution crystal structures reveal plasticity in the metal binding site of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease I.
He, H., Chen, Q., Georgiadis, M.M.(2014) Biochemistry 53: 6520-6529
- PubMed: 25251148
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500676p
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QH9, 4QHD, 4QHE - PubMed Abstract:
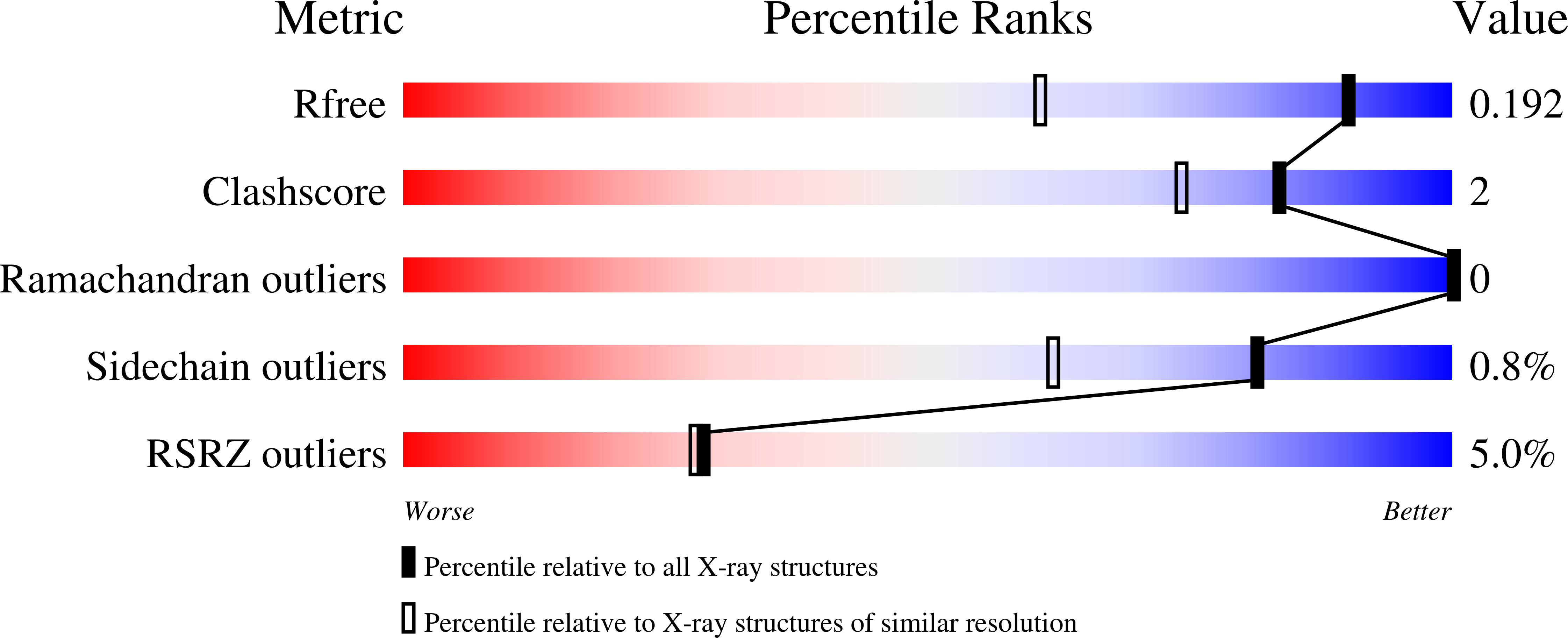
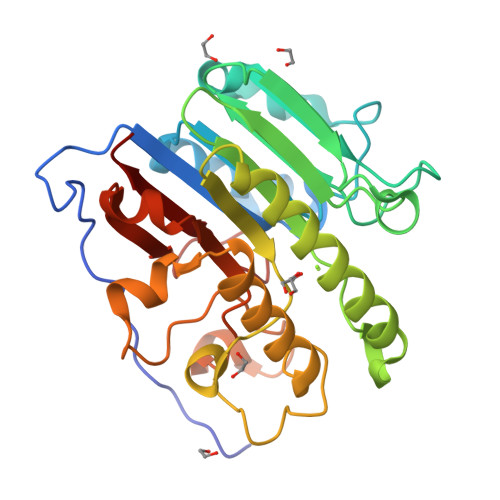
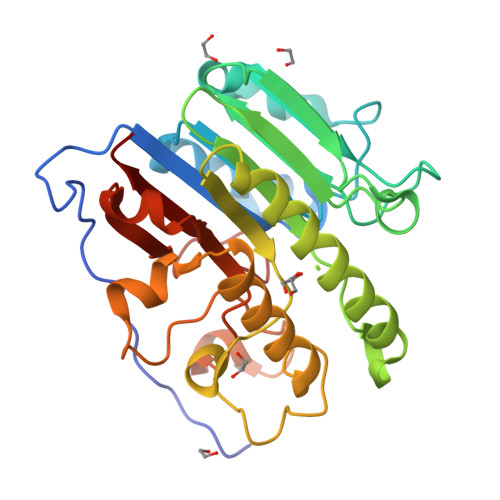
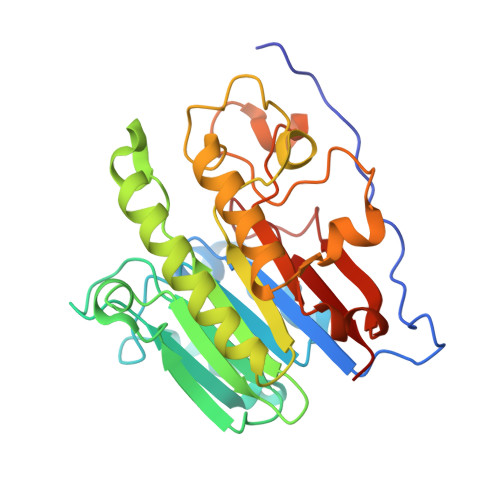
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease I (APE1) is an essential base excision repair enzyme that catalyzes a Mg²⁺-dependent reaction in which the phosphodiester backbone is cleaved 5' of an abasic site in duplex DNA. This reaction has been proposed to involve either one or two metal ions bound to the active site. In the present study, we report crystal structures of Mg²⁺, Mn²⁺, and apo-APE1 determined at 1.4, 2.2, and 1.65 Å, respectively, representing two of the highest resolution structures yet reported for APE1. In our structures, a single well-ordered Mn²⁺ ion was observed coordinated by D70 and E96; the Mg²⁺ site exhibited disorder modeled as two closely positioned sites coordinated by D70 and E96 or E96 alone. Direct metal binding analysis of wild-type, D70A, and E96A APE1, as assessed by differential scanning fluorimetry, indicated a role for D70 and E96 in binding of Mg²⁺ or Mn²⁺ to APE1. Consistent with the disorder exhibited by Mg²⁺ bound to the active site, two different conformations of E96 were observed coordinated to Mg²⁺. A third conformation for E96 in the apo structure is similar to that observed in the APE1-DNA-Mg²⁺ complex structure. Thus, binding of Mg²⁺ in three different positions within the active site of APE1 in these crystal structures corresponds directly with three different conformations of E96. Taken together, our results are consistent with the initial capture of metal by D70 and E96 and repositioning of Mg²⁺ facilitated by the structural plasticity of E96 in the active site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Indiana University School of Medicine , Indianapolis, Indiana 46202, United States.