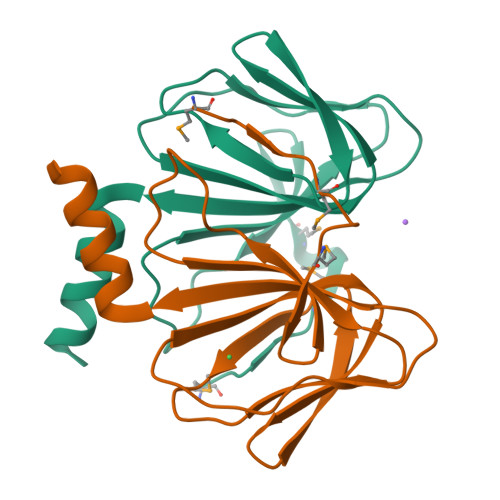
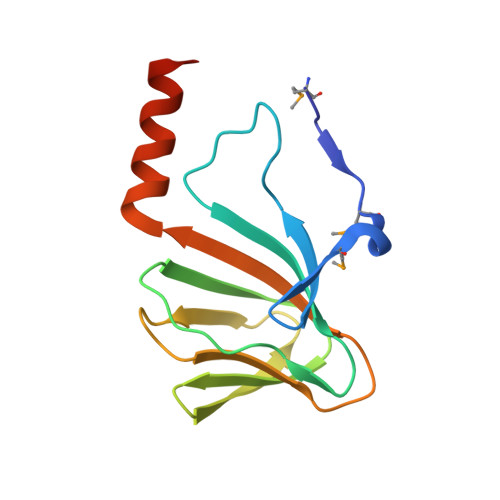
Structure of a cupin protein Plu4264 from Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. laumondii TTO1 at 1.35 angstrom resolution.
Weerth, R.S., Michalska, K., Bingman, C.A., Yennamalli, R.M., Li, H., Jedrzejczak, R., Wang, F., Babnigg, G., Joachimiak, A., Thomas, M.G., Phillips, G.N.(2015) Proteins 83: 383-388
- PubMed: 25354690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24705
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4MV2, 4Q29 - PubMed Abstract:
Proteins belonging to the cupin superfamily have a wide range of catalytic and noncatalytic functions. Cupin proteins commonly have the capacity to bind a metal ion with the metal frequently determining the function of the protein. We have been investigating the function of homologous cupin proteins that are conserved in more than 40 species of bacteria. To gain insights into the potential function of these proteins we have solved the structure of Plu4264 from Photorhabdus luminescens TTO1 at a resolution of 1.35 Å and identified manganese as the likely natural metal ligand of the protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bacteriology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin.