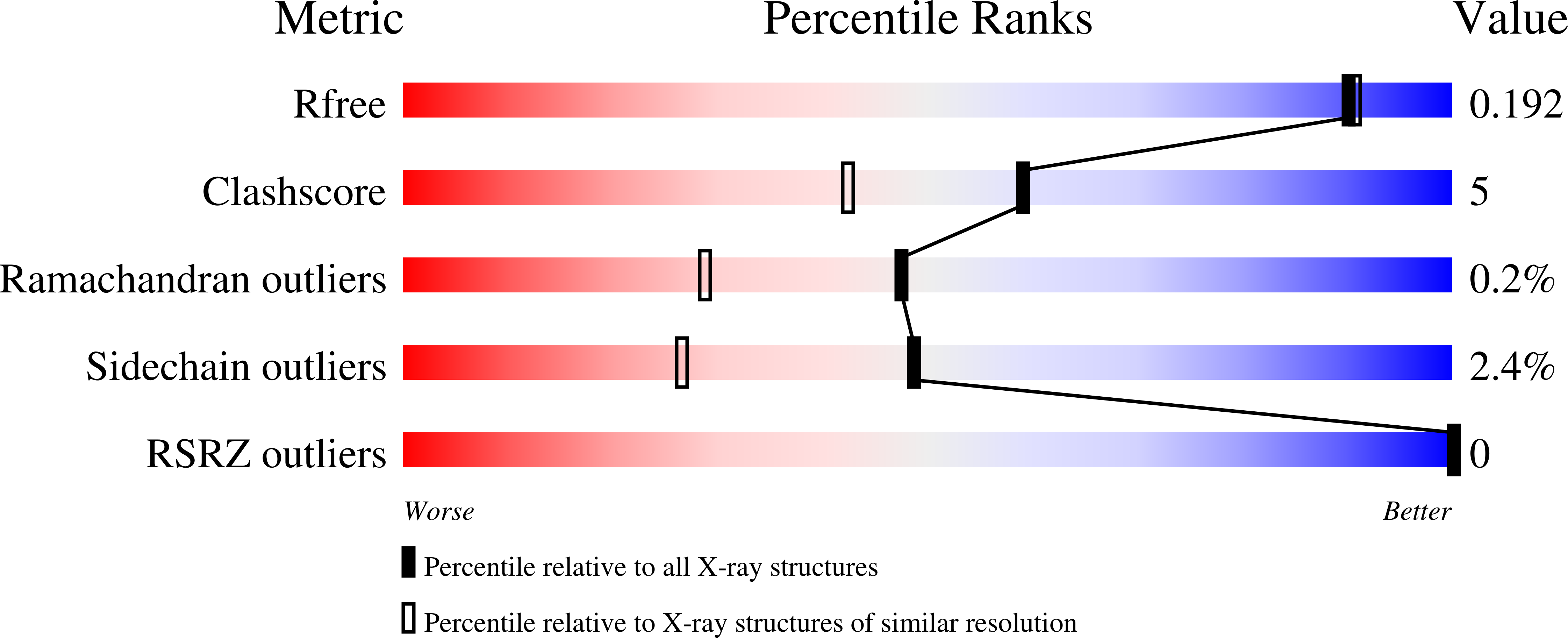
Structures of apo and product-bound human L-asparaginase: insights into the mechanism of autoproteolysis and substrate hydrolysis.
Nomme, J., Su, Y., Konrad, M., Lavie, A.(2012) Biochemistry 51: 6816-6826
- PubMed: 22861376
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi300870g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PVP, 4PVQ, 4PVR, 4PVS - PubMed Abstract:
Asparaginases catalyze the hydrolysis of the amino acid asparagine to aspartate and ammonia. Bacterial asparaginases are used in cancer chemotherapy to deplete asparagine from the blood, because several hematological malignancies depend on extracellular asparagine for growth. To avoid the immune response against the bacterial enzymes, it would be beneficial to replace them with human asparaginases. However, unlike the bacterial asparaginases, the human enzymes have a millimolar K(m) value for asparagine, making them inefficient in depleting the amino acid from blood. To facilitate the development of human variants suitable for therapeutic use, we determined the structure of human l-asparaginase (hASNase3). This asparaginase is an N-terminal nucleophile (Ntn) family member that requires autocleavage between Gly167 and Thr168 to become catalytically competent. For most Ntn hydrolases, this autoproteolytic activation occurs efficiently. In contrast, hASNas3 is relatively stable in its uncleaved state, and this allowed us to observe the structure of the enzyme prior to cleavage. To determine the structure of the cleaved state, we exploited our discovery that the free amino acid glycine promotes complete cleavage of hASNase3. Both enzyme states were elucidated in the absence and presence of the product aspartate. Together, these structures provide insight into the conformational changes required for cleavage and the precise enzyme-substrate interactions. The new understanding of hASNase3 will serve to guide the design of variants that possess a decreased K(m) value for asparagine, making the human enzyme a suitable replacement for the bacterial asparaginases in cancer therapy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL 60607, USA.