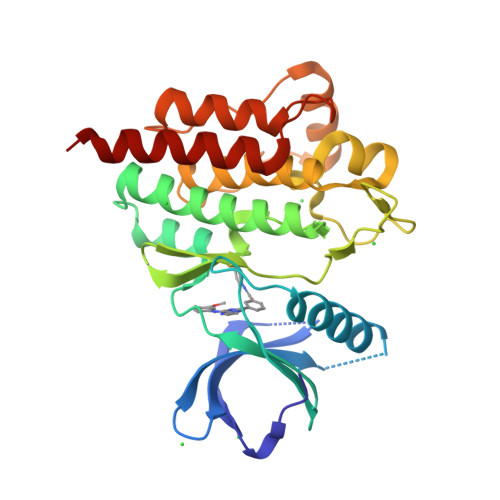
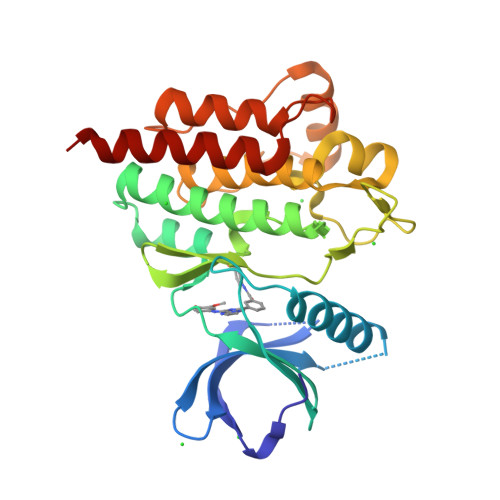
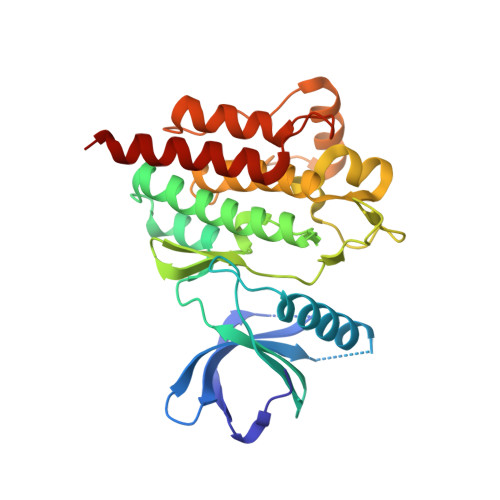
Discovery of GS-9973, a Selective and Orally Efficacious Inhibitor of Spleen Tyrosine Kinase.
Currie, K.S., Kropf, J.E., Lee, T., Blomgren, P., Xu, J., Zhao, Z., Gallion, S., Whitney, J.A., Maclin, D., Lansdon, E.B., Maciejewski, P., Rossi, A.M., Rong, H., Macaluso, J., Barbosa, J., Di Paolo, J.A., Mitchell, S.A.(2014) J Med Chem 57: 3856-3873
- PubMed: 24779514
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm500228a
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PUZ, 4PV0 - PubMed Abstract:
Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is an attractive drug target in autoimmune, inflammatory, and oncology disease indications. The most advanced Syk inhibitor, R406, 1 (or its prodrug form fostamatinib, 2), has shown efficacy in multiple therapeutic indications, but its clinical progress has been hampered by dose-limiting adverse effects that have been attributed, at least in part, to the off-target activities of 1. It is expected that a more selective Syk inhibitor would provide a greater therapeutic window. Herein we report the discovery and optimization of a novel series of imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazine Syk inhibitors. This work culminated in the identification of GS-9973, 68, a highly selective and orally efficacious Syk inhibitor which is currently undergoing clinical evaluation for autoimmune and oncology indications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, ‡Department of Biology, and §Department of Drug Metabolism, Gilead Sciences, Inc. , Branford, Connecticut 06405, United States.