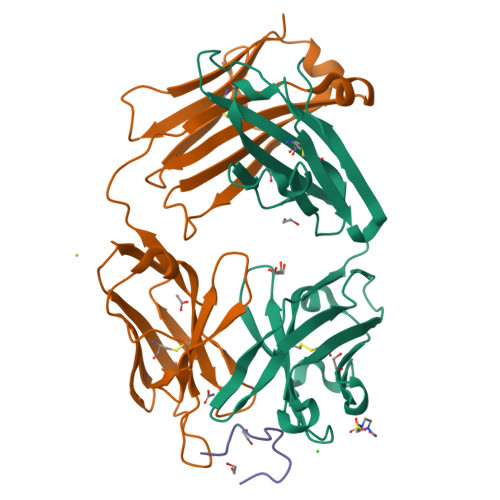
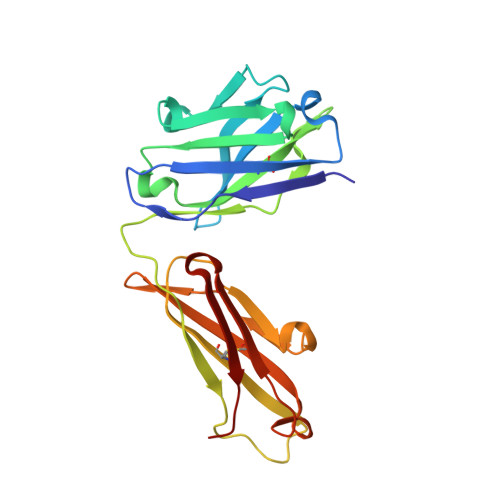
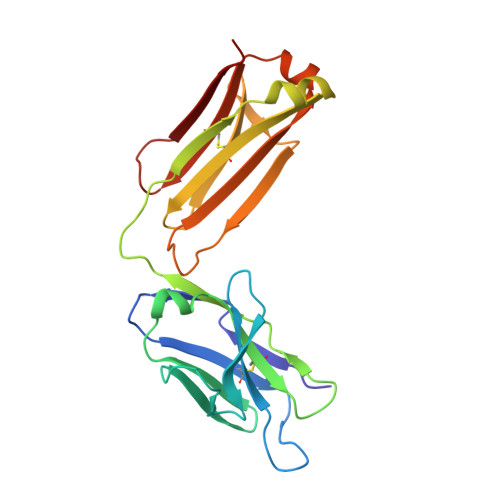
Inhibition mechanism of membrane metalloprotease by an exosite-swiveling conformational antibody.
Udi, Y., Grossman, M., Solomonov, I., Dym, O., Rozenberg, H., Moreno, V., Cuniasse, P., Dive, V., Arroyo, A.G., Sagi, I.(2015) Structure 23: 104-115
- PubMed: 25482542
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.10.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OUU, 4P3C, 4P3D, 4QXU - PubMed Abstract:
Membrane type 1 metalloprotease (MT1-MMP) is a membrane-anchored, zinc-dependent protease. MT1-MMP is an important mediator of cell migration and invasion, and overexpression of this enzyme has been correlated with the malignancy of various tumor types. Therefore, modulators of MT1-MMP activity are proposed to possess therapeutic potential in numerous invasive diseases. Here we report the inhibition mode of MT1-MMP by LEM-2/15 antibody, which targets a surface epitope of MT1-MMP. Specifically, the crystal structures of Fab LEM-2/15 in complex with the MT1-MMP surface antigen suggest that conformational swiveling of the enzyme surface loop is required for effective binding and consequent inhibition of MT1-MMP activity on the cell membrane. This inhibition mechanism appears to be effective in controlling active MT1-MMP in endothelial cells and at the leading edge of migratory cancer cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Regulation, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, Israel.