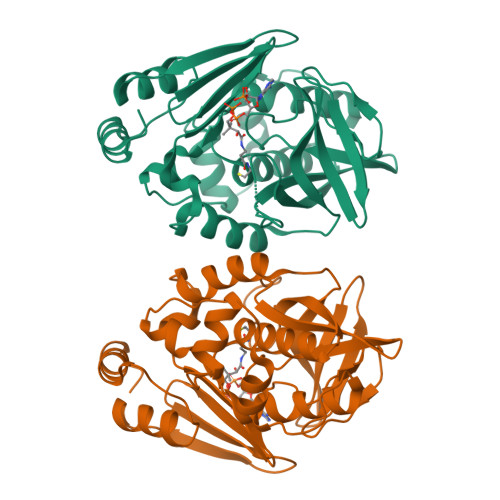
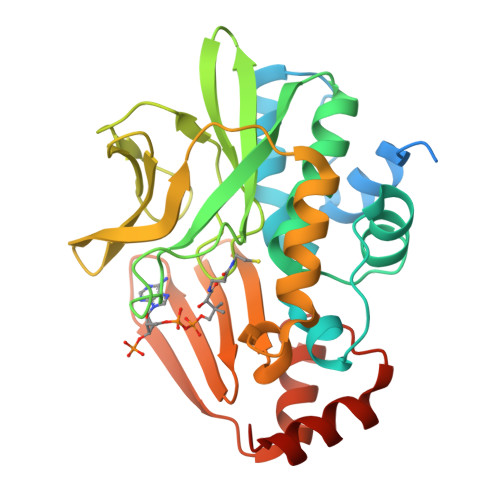
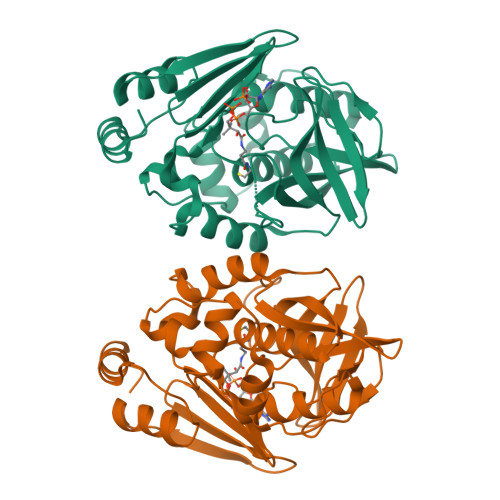
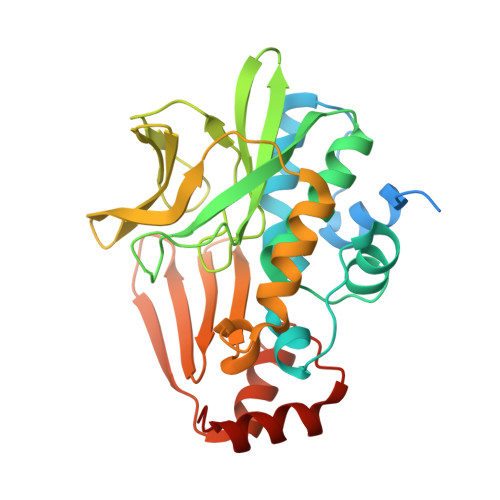
Insight into cofactor recognition in arylamine N-acetyltransferase enzymes: structure of Mesorhizobium loti arylamine N-acetyltransferase in complex with coenzyme A.
Xu, X., Li de la Sierra-Gallay, I., Kubiak, X., Duval, R., Chaffotte, A.F., Dupret, J.M., Haouz, A., Rodrigues-Lima, F.(2015) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71: 266-273
- PubMed: 25664736
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S139900471402522X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NV7, 4NV8 - PubMed Abstract:
Arylamine N-acetyltransferases (NATs) are xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes that catalyze the acetyl-CoA-dependent acetylation of arylamines. To better understand the mode of binding of the cofactor by this family of enzymes, the structure of Mesorhizobium loti NAT1 [(RHILO)NAT1] was determined in complex with CoA. The F42W mutant of (RHILO)NAT1 was used as it is well expressed in Escherichia coli and displays enzymatic properties similar to those of the wild type. The apo and holo structures of (RHILO)NAT1 F42W were solved at 1.8 and 2 Å resolution, respectively. As observed in the Mycobacterium marinum NAT1-CoA complex, in (RHILO)NAT1 CoA binding induces slight structural rearrangements that are mostly confined to certain residues of its `P-loop'. Importantly, it was found that the mode of binding of CoA is highly similar to that of M. marinum NAT1 but different from the modes reported for Bacillus anthracis NAT1 and Homo sapiens NAT2. Therefore, in contrast to previous data, this study shows that different orthologous NATs can bind their cofactors in a similar way, suggesting that the mode of binding CoA in this family of enzymes is less diverse than previously thought. Moreover, it supports the notion that the presence of the `mammalian/eukaryotic insertion loop' in certain NAT enzymes impacts the mode of binding CoA by imposing structural constraints.
Organizational Affiliation:
Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Unité BFA, CNRS UMR 8251, 75013 Paris, France.