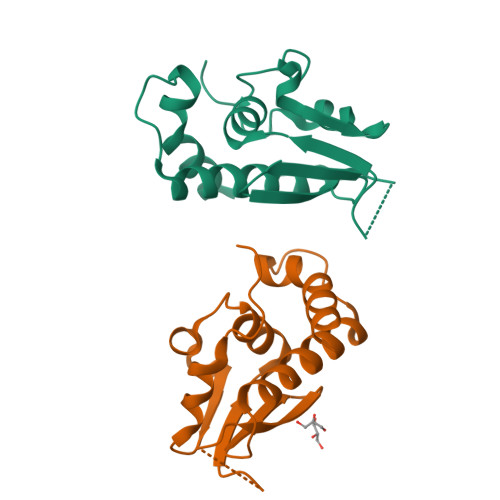
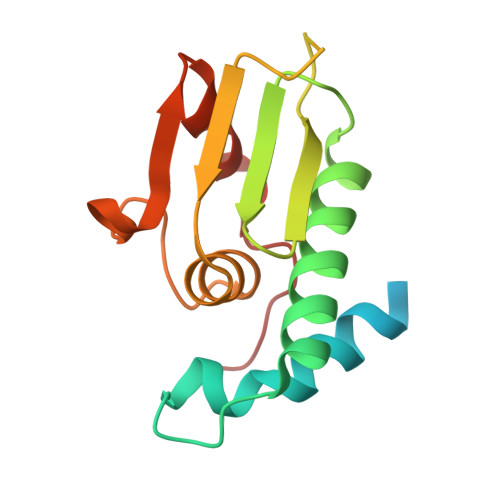
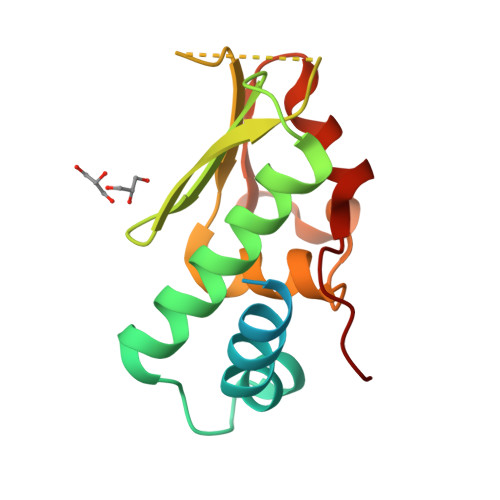
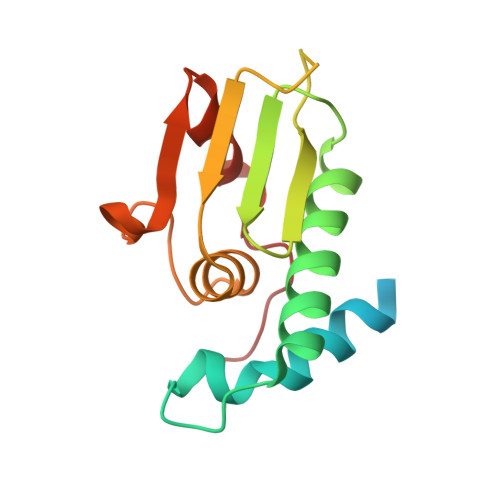
A structural and functional investigation of a novel protein from Mycobacterium smegmatis implicated in mycobacterial macrophage survivability.
Shahine, A., Littler, D., Brammananath, R., Chan, P.Y., Crellin, P.K., Coppel, R.L., Rossjohn, J., Beddoe, T.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 2264-2276
- PubMed: 25195741
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S139900471401092X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NSS - PubMed Abstract:
The success of pathogenic mycobacterial species is owing in part to their ability to parasitize the generally inhospitable phagosomal environment of host macrophages, utilizing a variety of strategies to avoid their antimycobacterial capabilities and thereby enabling their survival. A recently identified gene target in Mycobacterium smegmatis, highly conserved within Mycobacterium spp. and denoted MSMEG_5817, has been found to be important for bacterial survival within host macrophages. To gain insight into its function, the crystal structure of MSMEG_5817 has been solved to 2.40 Å resolution. The structure reveals a high level of structural homology to the sterol carrier protein (SCP) family, suggesting a potential role of MSMEG_5817 in the binding and transportation of biologically relevant lipids required for bacterial survival. The lipid-binding capacity of MSMEG_5817 was confirmed by ELISA, revealing binding to a number of phospholipids with varying binding specificities compared with Homo sapiens SCP. A potential lipid-binding site was probed by alanine-scanning mutagenesis, revealing structurally relevant residues and a binding mechanism potentially differing from that of the SCPs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria 3800, Australia.