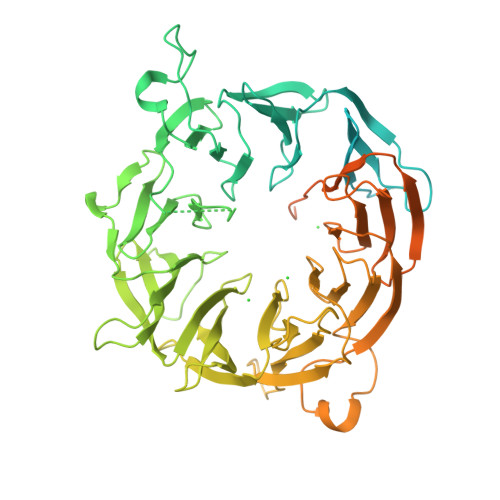
Translation initiation factor eIF3b contains a nine-bladed beta-propeller and interacts with the 40S ribosomal subunit
Liu, Y., Neumann, P., Kuhle, B., Monecke, T., Schell, S., Chari, A., Ficner, R.(2014) Structure 22: 923-930
- PubMed: 24768115
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.03.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NOX - PubMed Abstract:
The multisubunit eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, among which the subunit b (eIF3b) is a major scaffold protein, plays essential roles in protein synthesis. Here, we report the crystal structure of the WD40 domain of Chaetomium thermophilum eIF3b, revealing a nine-bladed β-propeller fold. Sequence analysis indicates that this propeller architecture is common to all eIF3b orthologs. Revisiting the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) map of the 43S preinitiation complex suggests an interaction of the eIF3b with the 40S ribosomal subunit involving the ribosomal protein S9e and the 18S rRNA. This model is strongly supported by the direct binding of eIF3b to 40S ribosomes and to the isolated ribosomal protein rpS9e in vitro.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Structural Biology, Institute for Microbiology and Genetics, GZMB, Georg-August-University Göttingen, 37077 Göttingen, Germany.