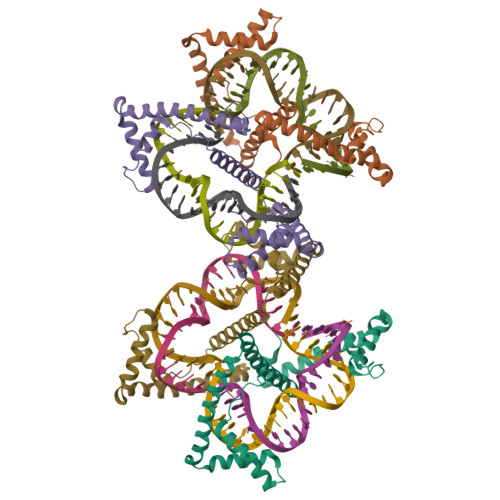
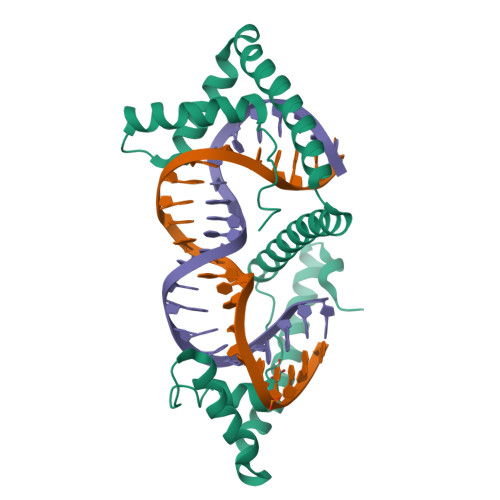
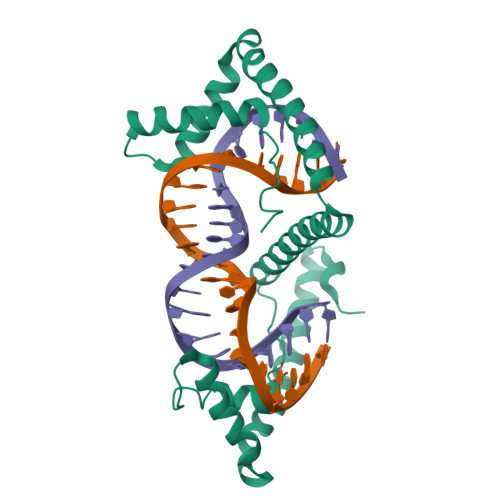
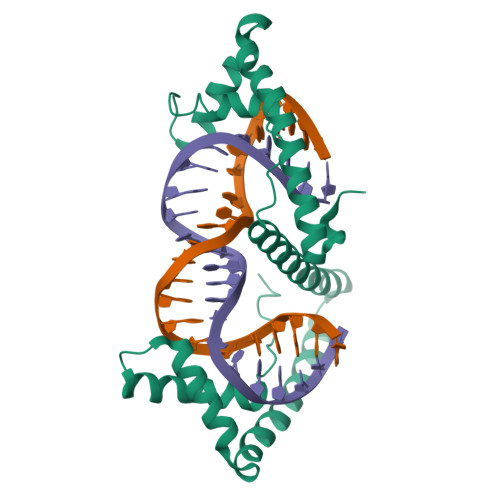
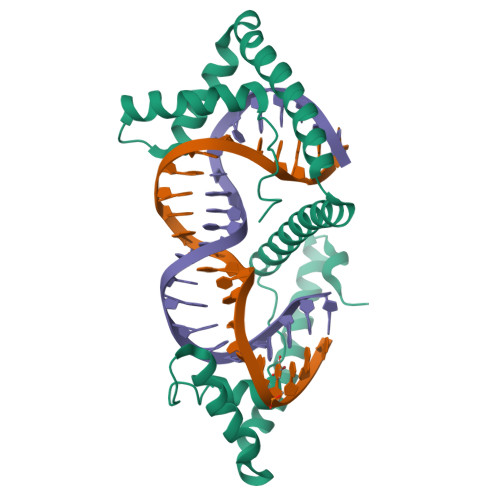
Distinct structural features of TFAM drive mitochondrial DNA packaging versus transcriptional activation.
Ngo, H.B., Lovely, G.A., Phillips, R., Chan, D.C.(2014) Nat Commun 5: 3077-3077
- PubMed: 24435062
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4077
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NNU, 4NOD - PubMed Abstract:
TFAM (transcription factor A, mitochondrial) is a DNA-binding protein that activates transcription at the two major promoters of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)--the light strand promoter (LSP) and the heavy strand promoter 1 (HSP1). Equally important, it coats and packages the mitochondrial genome. TFAM has been shown to impose a U-turn on LSP DNA; however, whether this distortion is relevant at other sites is unknown. Here we present crystal structures of TFAM bound to HSP1 and to nonspecific DNA. In both, TFAM similarly distorts the DNA into a U-turn. Yet, TFAM binds to HSP1 in the opposite orientation from LSP explaining why transcription from LSP requires DNA bending, whereas transcription at HSP1 does not. Moreover, the crystal structures reveal dimerization of DNA-bound TFAM. This dimerization is dispensable for DNA bending and transcriptional activation but is important in DNA compaction. We propose that TFAM dimerization enhances mitochondrial DNA compaction by promoting looping of the DNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Division of Biology and Biological Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California 91125, USA [2] Howard Hughes Medical Institute, California Institute of Technology, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91125, USA.