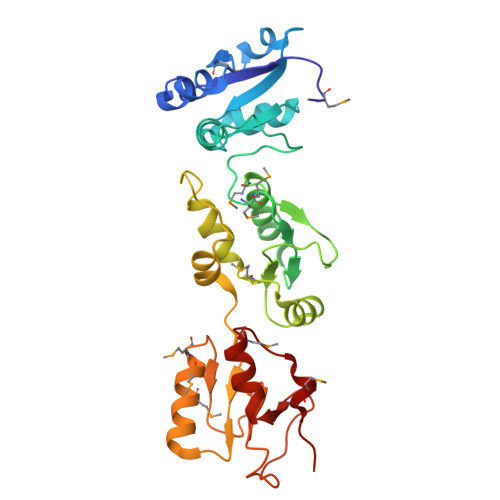
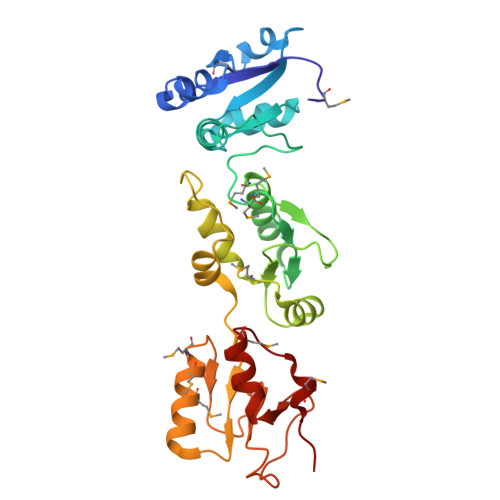
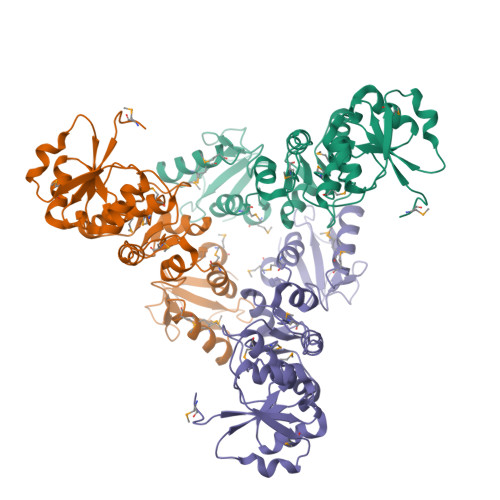
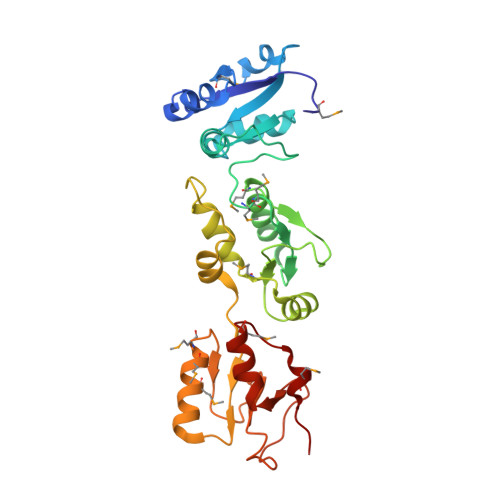
Crystal structure of triple-BRCT-domain of ECT2 and insights into the binding characteristics to CYK-4
Zou, Y., Shao, Z.H., Peng, J., Li, F.D., Gong, D., Wang, C., Zuo, X., Zhang, Z., Wu, J., Shi, Y., Gong, Q.(2014) FEBS Lett 588: 2911-2920
- PubMed: 25068414
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.07.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4N40 - PubMed Abstract:
Homo sapiens ECT2 is a cell cycle regulator that plays critical roles in cytokinesis. ECT2 activity is restrained during interphase via intra-molecular interactions that involve its N-terminal triple-BRCT-domain and its C-terminal DH-PH domain. At anaphase, this self-inhibitory mechanism is relieved by Plk1-phosphorylated CYK-4, which directly engages the ECT2 BRCT domain. To provide a structural perspective for this auto-inhibitory property, we solved the crystal structure of the ECT2 triple-BRCT-domain. In addition, we systematically analyzed the interaction between the ECT2 BRCT domains with phospho-peptides derived from its binding partner CYK-4, and have identified Ser164 as the major phospho-residue that links CYK-4 to the second ECT2 BRCT domain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China.