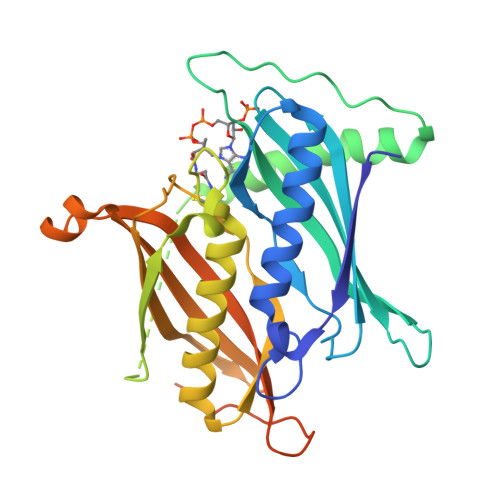
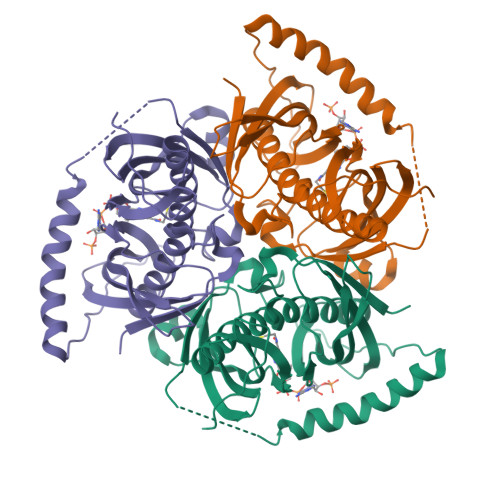
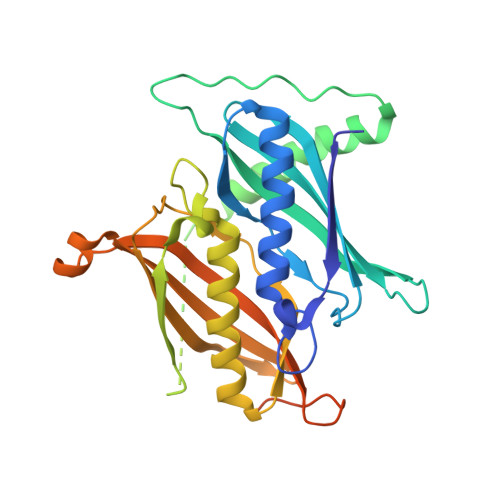
Structural basis for regulation of the human acetyl-CoA thioesterase 12 and interactions with the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein-related lipid transfer (START) domain.
Swarbrick, C.M., Roman, N., Cowieson, N., Patterson, E.I., Nanson, J., Siponen, M.I., Berglund, H., Lehtio, L., Forwood, J.K.(2014) J Biological Chem 289: 24263-24274
- PubMed: 25002576
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.589408
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4MOB, 4MOC - PubMed Abstract:
Acetyl-CoA plays a fundamental role in cell signaling and metabolic pathways, with its cellular levels tightly controlled through reciprocal regulation of enzymes that mediate its synthesis and catabolism. ACOT12, the primary acetyl-CoA thioesterase in the liver of human, mouse, and rat, is responsible for cleavage of the thioester bond within acetyl-CoA, producing acetate and coenzyme A for a range of cellular processes. The enzyme is regulated by ADP and ATP, which is believed to be mediated through the ligand-induced oligomerization of the thioesterase domains, whereby ATP induces active dimers and tetramers, whereas apo- and ADP-bound ACOT12 are monomeric and inactive. Here, using a range of structural and biophysical techniques, it is demonstrated that ACOT12 is a trimer rather than a tetramer and that neither ADP nor ATP exert their regulatory effects by altering the oligomeric status of the enzyme. Rather, the binding site and mechanism of ADP regulation have been determined to occur through two novel regulatory regions, one involving a large loop that links the thioesterase domains (Phe(154)-Thr(178)), defined here as RegLoop1, and a second region involving the C terminus of thioesterase domain 2 (Gln(304)-Gly(326)), designated RegLoop2. Mutagenesis confirmed that Arg(312) and Arg(313) are crucial for this mode of regulation, and novel interactions with the START domain are presented together with insights into domain swapping within eukaryotic thioesterases for substrate recognition. In summary, these experiments provide the first structural insights into the regulation of this enzyme family, revealing an alternate hypothesis likely to be conserved throughout evolution.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the School of Biomedical Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales 2678, Australia.