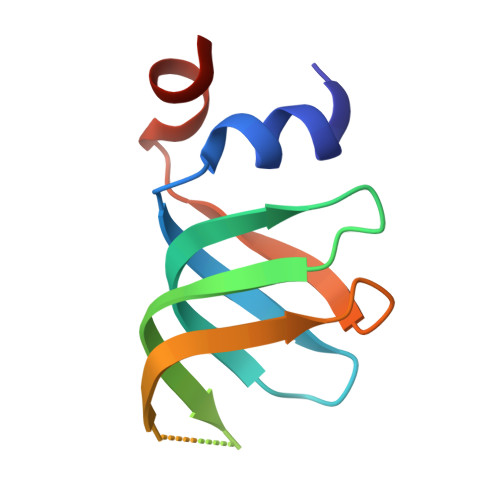
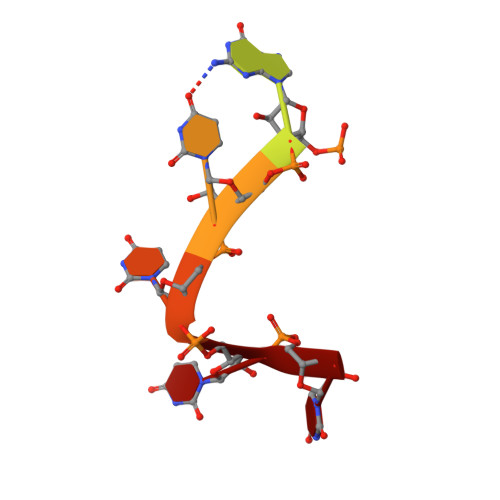
Crystal structures of the Lsm complex bound to the 3' end sequence of U6 small nuclear RNA.
Zhou, L., Hang, J., Zhou, Y., Wan, R., Lu, G., Yin, P., Yan, C., Shi, Y.(2014) Nature 506: 116-120
- PubMed: 24240276
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12803
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M75, 4M77, 4M78, 4M7A, 4M7D - PubMed Abstract:
Splicing of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) in eukaryotic cells is carried out by the spliceosome, which consists of five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) and a number of accessory factors and enzymes. Each snRNP contains a ring-shaped subcomplex of seven proteins and a specific RNA molecule. The U6 snRNP contains a unique heptameric Lsm protein complex, which specifically recognizes the U6 small nuclear RNA at its 3' end. Here we report the crystal structures of the heptameric Lsm complex, both by itself and in complex with a 3' fragment of U6 snRNA, at 2.8 Å resolution. Each of the seven Lsm proteins interacts with two neighbouring Lsm components to form a doughnut-shaped assembly, with the order Lsm3-2-8-4-7-5-6. The four uridine nucleotides at the 3' end of U6 snRNA are modularly recognized by Lsm3, Lsm2, Lsm8 and Lsm4, with the uracil base specificity conferred by a highly conserved asparagine residue. The uracil base at the extreme 3' end is sandwiched by His 36 and Arg 69 from Lsm3, through π-π and cation-π interactions, respectively. The distinctive end-recognition of U6 snRNA by the Lsm complex contrasts with RNA binding by the Sm complex in the other snRNPs. The structural features and associated biochemical analyses deepen mechanistic understanding of the U6 snRNP function in pre-mRNA splicing.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Protein Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China [2] Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Center for Structural Biology, School of Life Sciences and School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China [3].