Structural Basis for the Interaction between the Potato Virus X Resistance Protein (Rx) and Its Cofactor Ran GTPase-activating Protein 2 (RanGAP2)
Hao, W., Collier, S.M., Moffett, P., Chai, J.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 35868-35876
- PubMed: 24194517
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.517417
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M70 - PubMed Abstract:
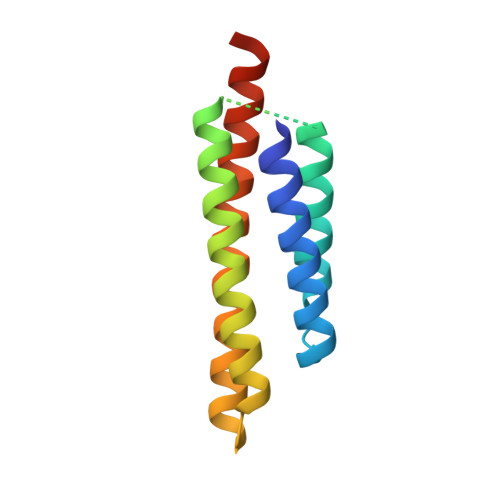
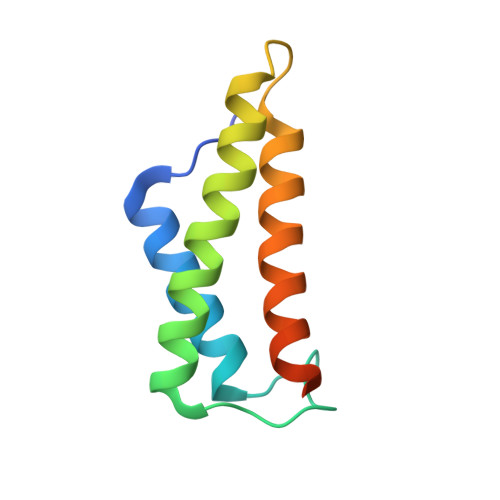
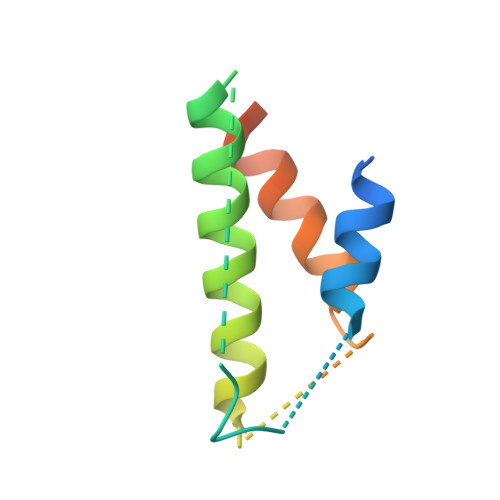
The potato (Solanum tuberosum) disease resistance protein Rx has a modular arrangement that contains coiled-coil (CC), nucleotide-binding (NB), and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains and mediates resistance to potato virus X. The Rx N-terminal CC domain undergoes an intramolecular interaction with the Rx NB-LRR region and an intermolecular interaction with the Rx cofactor RanGAP2 (Ran GTPase-activating protein 2). Here, we report the crystal structure of the Rx CC domain in complex with the Trp-Pro-Pro (WPP) domain of RanGAP2. The structure reveals that the Rx CC domain forms a heterodimer with RanGAP2, in striking contrast to the homodimeric structure of the CC domain of the barley disease resistance protein MLA10. Structure-based mutagenesis identified residues from both the Rx CC domain and the RanGAP2 WPP domain that are crucial for their interaction and function in vitro and in vivo. Our results reveal the molecular mechanism underlying the interaction of Rx with RanGAP2 and identify the distinct surfaces of the Rx CC domain that are involved in intramolecular and intermolecular interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China.