Structural basis of allosteric interactions among Ca(2+)-binding sites in a K(+) channel RCK domain.
Smith, F.J., Pau, V.P., Cingolani, G., Rothberg, B.S.(2013) Nat Commun 4: 2621-2621
- PubMed: 24126388
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3621
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4L73, 4L74, 4L75, 4L76 - PubMed Abstract:
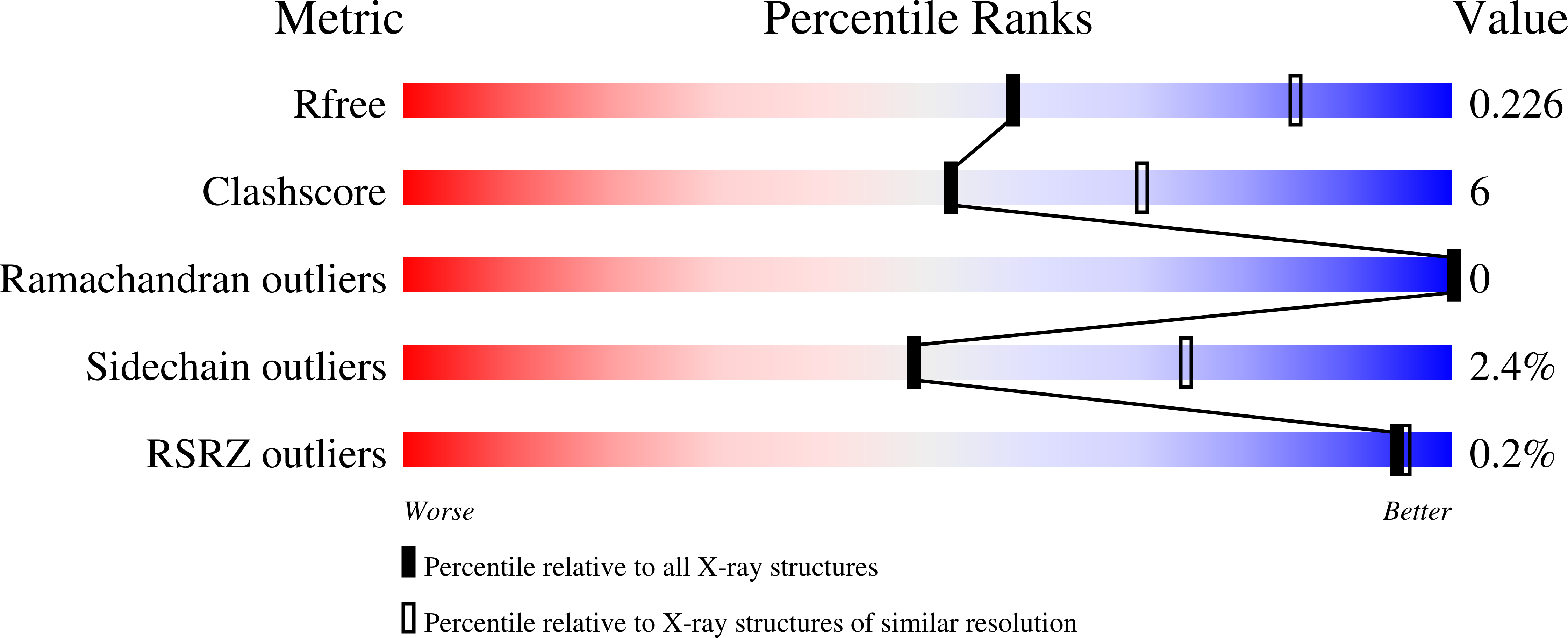
Ligand binding sites within proteins can interact by allosteric mechanisms to modulate binding affinities and control protein function. Here we present crystal structures of the regulator of K+ conductance (RCK) domain from a K+ channel, MthK, which reveal the structural basis of allosteric coupling between two Ca2+ regulatory sites within the domain. Comparison of RCK domain crystal structures in a range of conformations and with different numbers of regulatory Ca2+ ions bound, combined with complementary electrophysiological analysis of channel gating, suggests chemical interactions that are important for modulation of ligand binding and subsequent channel opening.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Temple University School of Medicine, 3400 North Broad Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19140, USA.