Discovery of a new genetic variant of methionine aminopeptidase from streptococci with possible post-translational modifications: biochemical and structural characterization.
Arya, T., Kishor, C., Saddanapu, V., Reddi, R., Addlagatta, A.(2013) PLoS One 8: e75207-e75207
- PubMed: 24124477
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075207
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4KM3 - PubMed Abstract:
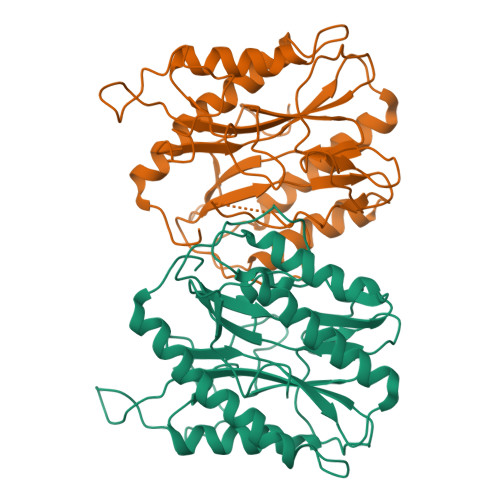
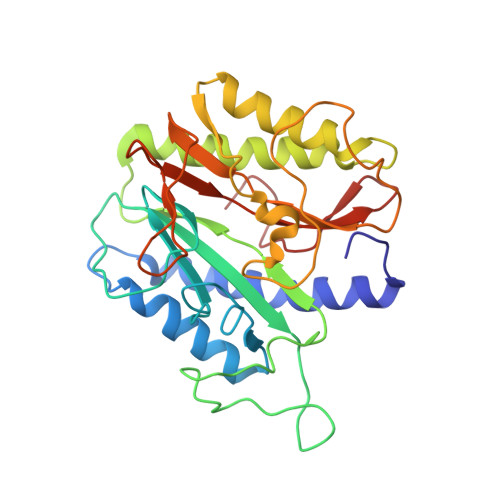
Protein N-terminal methionine excision is an essential co-translational process that occurs in the cytoplasm of all organisms. About 60-70% of the newly synthesized proteins undergo this modification. Enzyme responsible for the removal of initiator methionine is methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP), which is a dinuclear metalloprotease. This protein is conserved through all forms of life from bacteria to human except viruses. MetAP is classified into two isoforms, Type I and II. Removal of the map gene or chemical inhibition is lethal to bacteria and to human cell lines, suggesting that MetAP could be a good drug target. In the present study we describe the discovery of a new genetic variant of the Type I MetAP that is present predominantly in the streptococci bacteria. There are two inserts (insert one: 27 amino acids and insert two: four residues) within the catalytic domain. Possible glycosylation and phosphorylation posttranslational modification sites are identified in the 'insert one'. Biochemical characterization suggests that this enzyme behaves similar to other MetAPs in terms of substrate specificity. Crystal structure Type Ia MetAP from Streptococcus pneumoniae (SpMetAP1a) revealed that it contains two molecules in the asymmetric unit and well ordered inserts with structural features that corroborate the possible posttranslational modification. Both the new inserts found in the SpMetAP1a structurally align with the P-X-X-P motif found in the M. tuberculosis and human Type I MetAPs as well as the 60 amino acid insert in the human Type II enzyme suggesting possible common function. In addition, one of the β-hairpins within in the catalytic domain undergoes a flip placing a residue which is essential for enzyme activity away from the active site and the β-hairpin loop of this secondary structure in the active site obstructing substrate binding. This is the first example of a MetAP crystallizing in the inactive form.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Chemical Biology, CSIR-Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India.