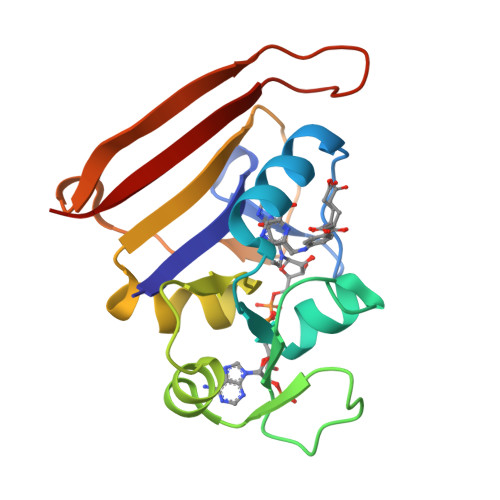
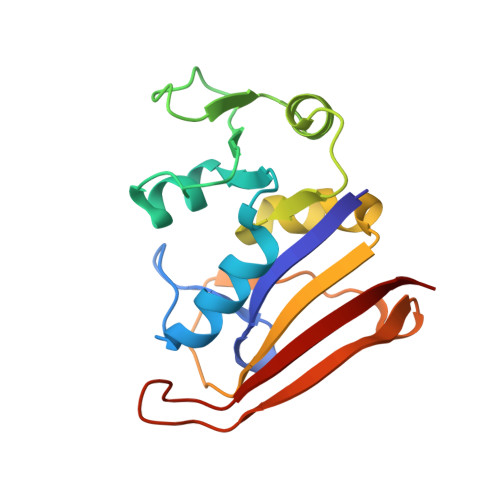
Automated identification of functional dynamic contact networks from X-ray crystallography.
van den Bedem, H., Bhabha, G., Yang, K., Wright, P.E., Fraser, J.S.(2013) Nat Methods 10: 896-902
- PubMed: 23913260
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2592
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4KJJ, 4KJK, 4KJL - PubMed Abstract:
Protein function often depends on the exchange between conformational substates. Allosteric ligand binding or distal mutations can stabilize specific active-site conformations and consequently alter protein function. Observing alternative conformations at low levels of electron density, in addition to comparison of independently determined X-ray crystal structures, can provide mechanistic insights into conformational dynamics. Here we report a new algorithm, CONTACT, that identifies contact networks of conformationally heterogeneous residues directly from high-resolution X-ray crystallography data. Contact networks determined for Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase (ecDHFR) predict the observed long-range pattern of NMR chemical shift perturbations of an allosteric mutation. A comparison of contact networks in wild-type and mutant ecDHFR suggests that mutations that alter optimized contact networks of coordinated motions can impair catalytic function. CONTACT-guided mutagenesis can exploit the structure-dynamics-function relationship in protein engineering and design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Joint Center for Structural Genomics, Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, Stanford, California, USA. vdbedem@slac.stanford.edu