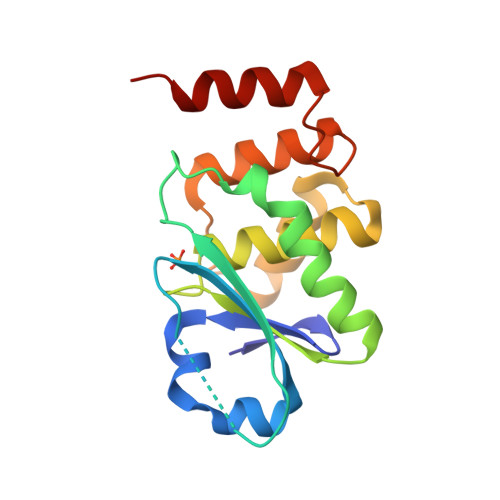
The family-wide structure and function of human dual-specificity protein phosphatases
Jeong, D.G., Wei, C.H., Ku, B., Jeon, T.J., Chien, P.N., Kim, J.K., Park, S.Y., Hwang, H.S., Ryu, S.Y., Park, H., Kim, D.S., Kim, S.J., Ryu, S.E.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 421-435
- PubMed: 24531476
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713029866
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JMJ, 4JMK, 4JNB, 4KI9 - PubMed Abstract:
Dual-specificity protein phosphatases (DUSPs), which dephosphorylate both phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine, play vital roles in immune activation, brain function and cell-growth signalling. A family-wide structural library of human DUSPs was constructed based on experimental structure determination supplemented with homology modelling. The catalytic domain of each individual DUSP has characteristic features in the active site and in surface-charge distribution, indicating substrate-interaction specificity. The active-site loop-to-strand switch occurs in a subtype-specific manner, indicating that the switch process is necessary for characteristic substrate interactions in the corresponding DUSPs. A comprehensive analysis of the activity-inhibition profile and active-site geometry of DUSPs revealed a novel role of the active-pocket structure in the substrate specificity of DUSPs. A structure-based analysis of redox responses indicated that the additional cysteine residues are important for the protection of enzyme activity. The family-wide structures of DUSPs form a basis for the understanding of phosphorylation-mediated signal transduction and the development of therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medical Proteomics Research Center, KRIBB, Daejeon, Republic of Korea.