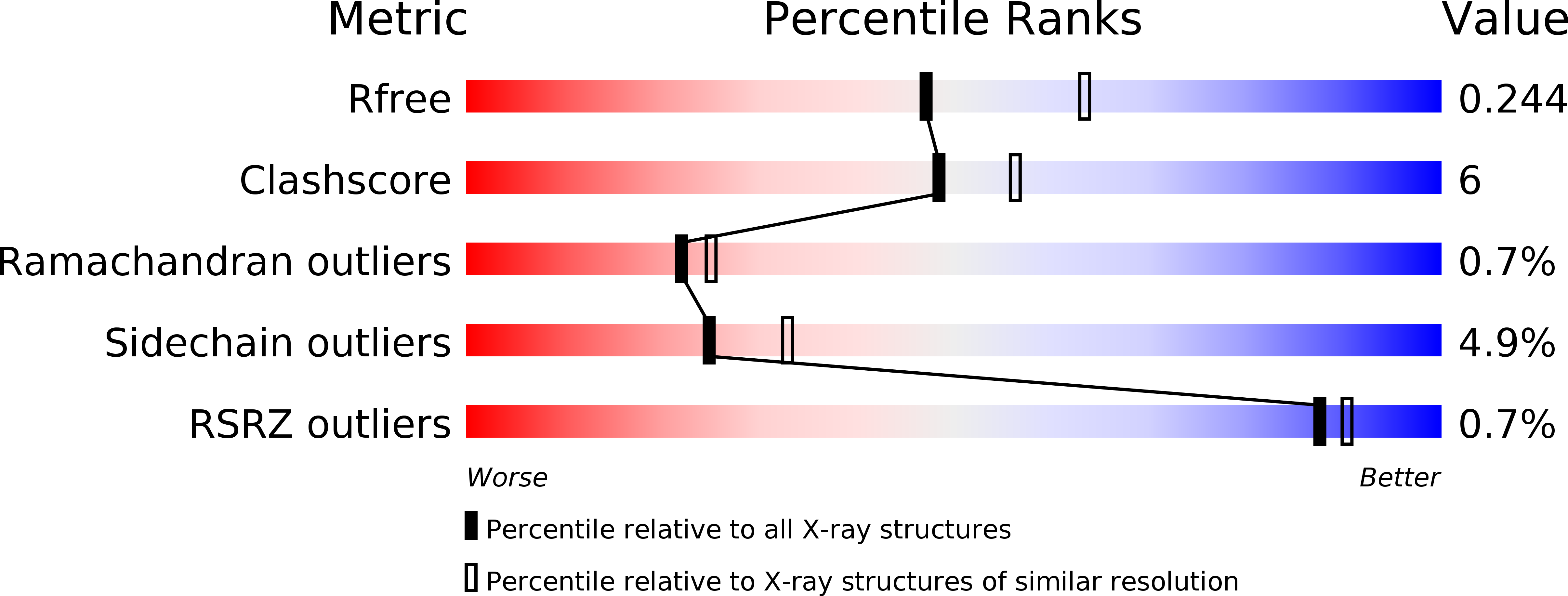
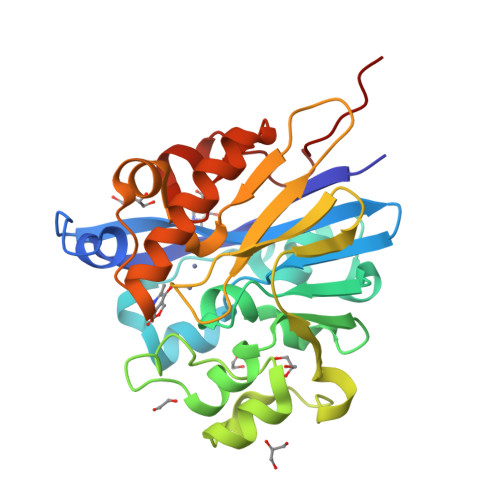
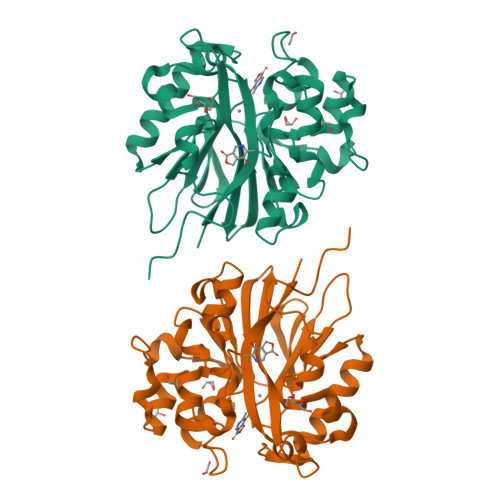
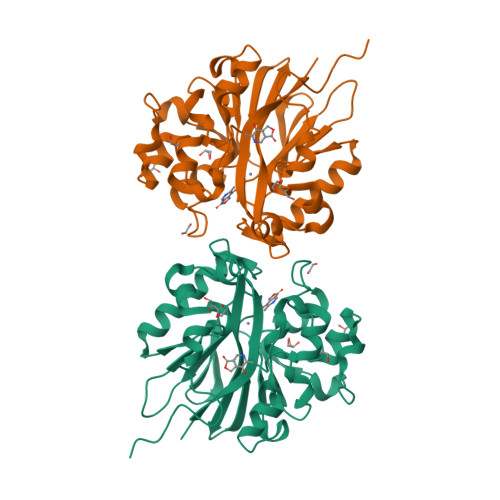
Structure of 4-pyridoxolactonase from Mesorhizobium loti.
Kobayashi, J., Yoshikane, Y., Yagi, T., Baba, S., Mizutani, K., Takahashi, N., Mikami, B.(2014) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 70: 424-432
- PubMed: 24699732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X14003926
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AJ3, 4KEP, 4KEQ - PubMed Abstract:
4-Pyridoxolactonase from Mesorhizobium loti catalyzes the zinc-dependent lactone-ring hydrolysis of 4-pyridoxolactone (4PAL) to 4-pyridoxic acid (4PA) in vitamin B6 degradation pathway I. The crystal structures of 4-pyridoxolactonase and its complex with 5-pyridoxolactone (5PAL; the competitive inhibitor) were determined. The overall structure was an αβ/βα sandwich fold, and two zinc ions were coordinated. This strongly suggested that the enzyme belongs to subclass B3 of the class B β-lactamases. In the complex structure, the carbonyl group of 5PAL pointed away from the active site, revealing why it acts as a competitive inhibitor. Based on docking simulation with 4PAL, 4PA and a reaction intermediate, 4-pyridoxolactonase probably catalyzes the reaction through a subclass B2-like mechanism, not the subclass B3 mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Applied Structural Biology, Division of Applied Life Sciences, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Gokasyo, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan.