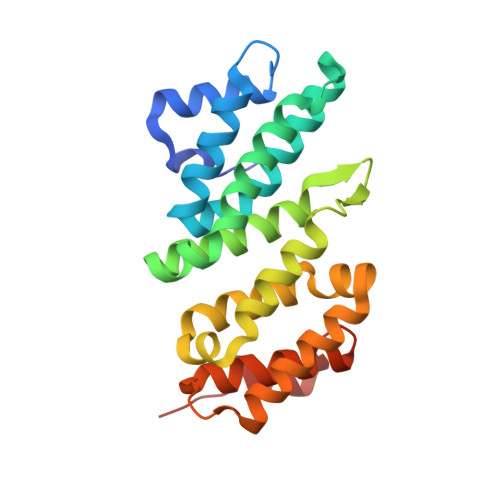
Structural and biochemical studies of SLIP1-SLBP identify DBP5 and eIF3g as SLIP1-binding proteins.
von Moeller, H., Lerner, R., Ricciardi, A., Basquin, C., Marzluff, W.F., Conti, E.(2013) Nucleic Acids Res 41: 7960-7971
- PubMed: 23804756
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt558
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JHJ, 4JHK - PubMed Abstract:
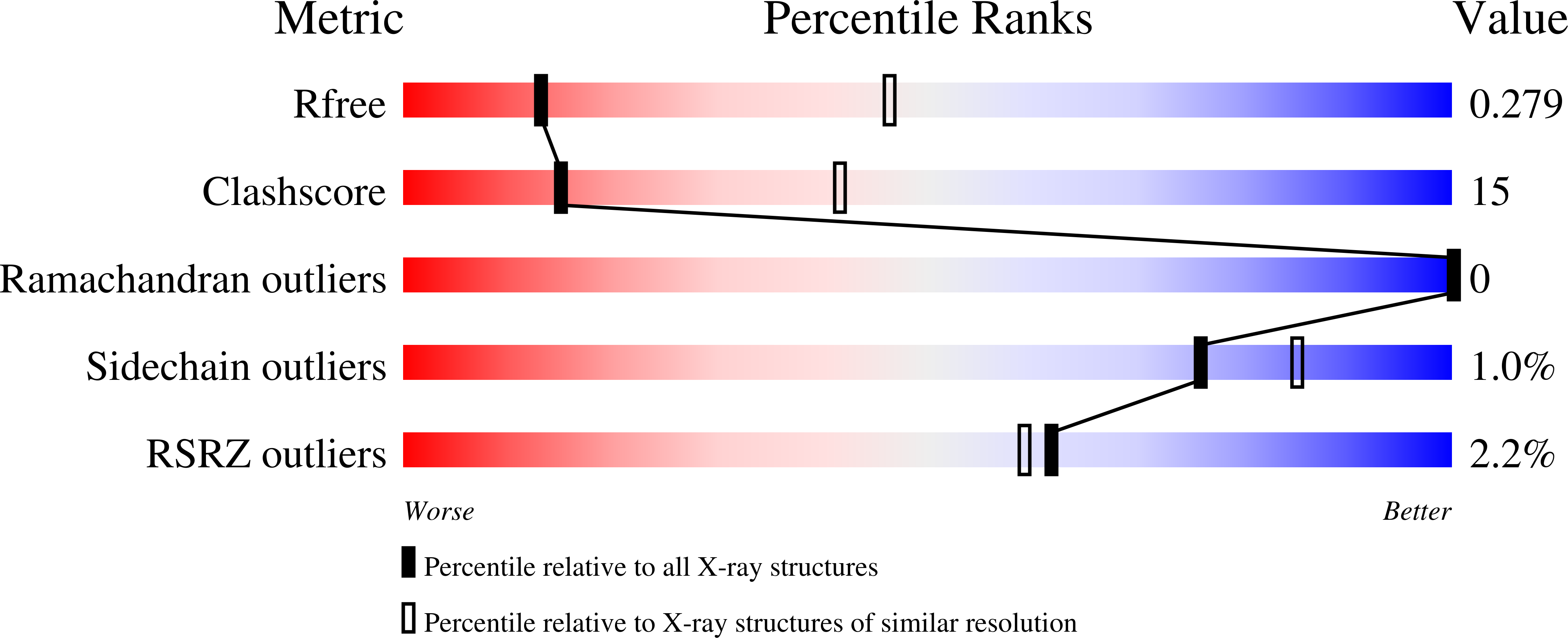
In metazoans, replication-dependent histone mRNAs end in a stem-loop structure instead of the poly(A) tail characteristic of all other mature mRNAs. This specialized 3' end is bound by stem-loop binding protein (SLBP), a protein that participates in the nuclear export and translation of histone mRNAs. The translational activity of SLBP is mediated by interaction with SLIP1, a middle domain of initiation factor 4G (MIF4G)-like protein that connects to translation initiation. We determined the 2.5 Å resolution crystal structure of zebrafish SLIP1 bound to the translation-activation domain of SLBP and identified the determinants of the recognition. We discovered a SLIP1-binding motif (SBM) in two additional proteins: the translation initiation factor eIF3g and the mRNA-export factor DBP5. We confirmed the binding of SLIP1 to DBP5 and eIF3g by pull-down assays and determined the 3.25 Å resolution structure of SLIP1 bound to the DBP5 SBM. The SBM-binding and homodimerization residues of SLIP1 are conserved in the MIF4G domain of CBP80/20-dependent translation initiation factor (CTIF). The results suggest how the SLIP1 homodimer or a SLIP1-CTIF heterodimer can function as platforms to bridge SLBP with SBM-containing proteins involved in different steps of mRNA metabolism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Cell Biology Department, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, Munich, D-82152 Germany and Program in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599, USA.