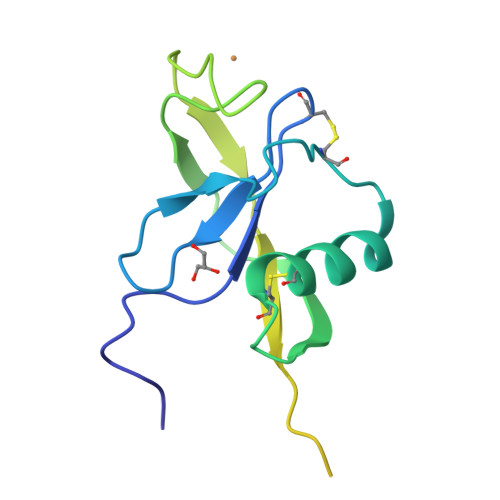
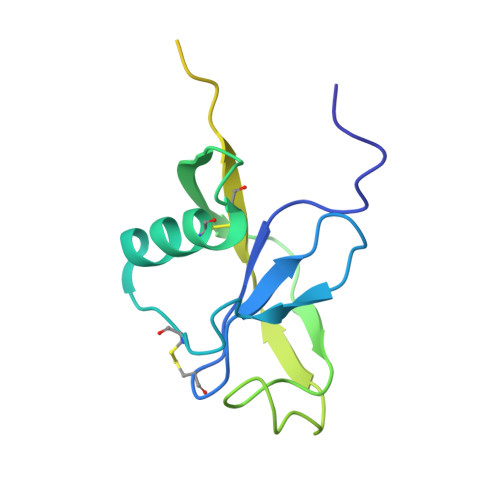
Amyloid precursor protein dimerization and synaptogenic function depend on copper binding to the growth factor-like domain
Baumkotter, F., Schmidt, N., Vargas, C., Schilling, S., Weber, R., Wagner, K., Fiedler, S., Klug, W., Radzimanowski, J., Nickolaus, S., Keller, S., Eggert, S., Wild, K., Kins, S.(2014) J Neurosci 34: 11159-11172
- PubMed: 25122912
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0180-14.2014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JFN - PubMed Abstract:
Accumulating evidence suggests that the copper-binding amyloid precursor protein (APP) has an essential synaptic function. APP synaptogenic function depends on trans-directed dimerization of the extracellular E1 domain encompassing a growth factor-like domain (GFLD) and a copper-binding domain (CuBD). Here we report the 1.75 Å crystal structure of the GFLD in complex with a copper ion bound with high affinity to an extended hairpin loop at the dimerization interface. In coimmunoprecipitation assays copper binding promotes APP interaction, whereas mutations in the copper-binding sites of either the GFLD or CuBD result in a drastic reduction in APP cis-orientated dimerization. We show that copper is essential and sufficient to induce trans-directed dimerization of purified APP. Furthermore, a mixed culture assay of primary neurons with HEK293 cells expressing different APP mutants revealed that APP potently promotes synaptogenesis depending on copper binding to the GFLD. Together, these findings demonstrate that copper binding to the GFLD of APP is required for APP cis-/trans-directed dimerization and APP synaptogenic function. Thus, neuronal activity or disease-associated changes in copper homeostasis likely go along with altered APP synaptic function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Human Biology and Human Genetics.